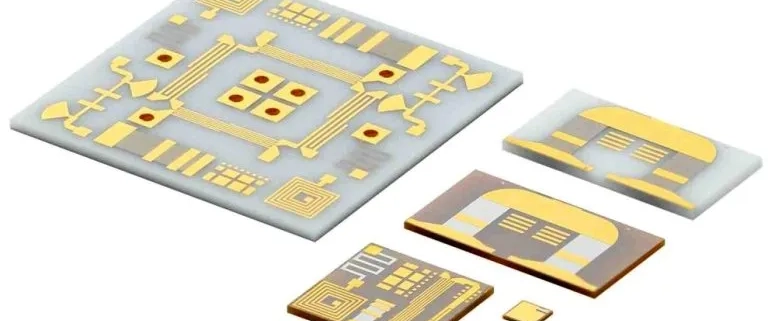
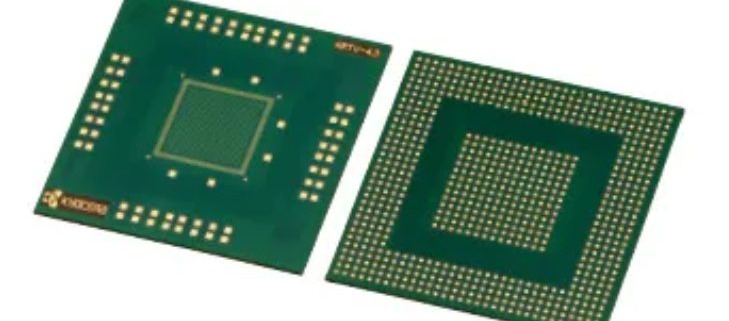
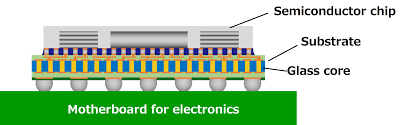
A Ceramic Substrate Circuit Board is an advanced type of PCB known for its exceptional thermal and mechanical properties, making it vital in modern electronics. Unlike traditional materials like FR4, ceramic substrates offer high-temperature resistance and superior thermal conductivity, allowing for effective heat dissipation in demanding applications. These unique properties enable ceramic substrates to maintain stability and reliability even in extreme operating conditions, which is critical for high-performance electronics.
Due to these advantages, Ceramic Substrate Circuit Boards are widely used in power electronics, where efficient thermal management is essential to prevent overheating. They are also preferred in high-frequency devices and advanced electronic systems, as the material’s excellent electrical insulation supports stable signal transmission. With their robust performance characteristics, ceramic substrate boards are key components in cutting-edge applications, providing essential support for industries that require both durability and precision in their electronic components.
阅读更多