In modern electronics, printed circuit boards (PCBs) serve as the essential backbone for connecting and supporting electronic components. They provide mechanical stability, electrical pathways, and thermal management critical to the reliable operation of devices ranging from consumer gadgets to industrial systems. Among the various safety and performance standards, the 94V-0 flammability rating—defined by the UL 94 standard—plays a crucial role in certifying that a PCB material can resist fire hazards. A material rated as 94V-0 self-extinguishes quickly and does not drip flaming particles, making it ideal for consumer safety and compliance in regulated markets. As devices increasingly demand higher power and thermal efficiency, the use of 94v0 metal substrate PCB solutions has grown significantly. These boards combine flame-retardant properties with enhanced heat dissipation, making them especially valuable in applications like LED lighting, automotive electronics, and power converters where thermal management is vital. 阅读更多
In PCB manufacturing, a rigid substrate refers to a solid, non-flexible base material—typically FR4—that provides structural support and mechanical stability to printed circuit boards. Unlike flexible substrates, rigid substrates maintain their shape during assembly and use, making them ideal for most consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and communication modules. Among the various available thicknesses, the 0.8mm thick rigid substrate core stands out as a popular choice for compact and lightweight applications. It offers a balance between mechanical strength and space-saving design, which is especially valuable in wearable devices, sensor modules, and high-density PCB layouts. This thickness allows for easier microvia drilling, better thermal management, and cost-effective production in multi-layer designs. The purpose of this article is to help engineers, product designers, and procurement professionals understand the role, advantages, and considerations of choosing a 0.8mm thick rigid substrate core in PCB projects, and how it compares to other commonly used core thicknesses.
FR4 is a widely used composite material made from woven fiberglass cloth and epoxy resin, known for its excellent mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and electrical insulation properties. It serves as the standard substrate for printed circuit boards (PCBs) across a broad range of electronic applications. Among the many variations available, the 0.8mm FR4 substrate without copper has gained attention for specific industrial and prototyping needs. This particular form eliminates the copper foil typically used for conductive pathways, making it ideal for applications where electrical insulation, rather than conductivity, is required. The reduced 0.8mm thickness offers a balance between flexibility and rigidity, which is crucial in compact electronic assemblies. Common use cases for the 0.8mm FR4 substrate without copper include insulation layers in multilayer PCBs, dielectric spacers in RF designs, and mechanical support plates for non-conductive structural parts. Its cost-effectiveness and processing simplicity further add to its appeal in specialized manufacturing scenarios. 阅读更多
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the foundation of modern electronics, providing essential structural support and electrical connectivity for countless devices. However, as electronic components become smaller and more powerful, managing heat dissipation has become a significant challenge. Excessive heat can lead to reduced performance, shortened component lifespan, and even system failure. To address these challenges, MCPCB (Metal Core Printed Circuit Board) technology has emerged as a highly effective thermal solution. By incorporating a metal core, typically aluminum or copper, MCPCBs significantly enhance thermal conductivity compared to standard FR-4 boards. Central to this improvement is the use of thermal substrates mcpcb, which integrate an insulating layer with excellent heat transfer properties between the circuit and the metal base. This specialized structure ensures efficient thermal management, making thermal substrates mcpcb critical for high-power applications such as LED lighting, automotive electronics, and power supplies. 阅读更多
In today’s rapidly evolving electronics industry, PCB materials play a critical role in ensuring the performance, reliability, and efficiency of electronic devices. High-frequency and high-speed applications, such as 5G communication systems, radar, and satellite technologies, demand materials with exceptional electrical and thermal properties. Among the leading innovators in this space is Taconic, a globally recognized manufacturer specializing in high-performance RF PCB materials. Taconic’s decades of expertise have made it a trusted name for industries requiring precision and stability at microwave and millimeter-wave frequencies. This article is designed to provide a thorough understanding of taconic rf substrates, covering their material composition, unique properties, common applications, and why they are preferred over traditional PCB materials. Whether you are an engineer, designer, or project manager, gaining insight into taconic rf substrates will help you make better decisions when working on high-frequency electronic designs.
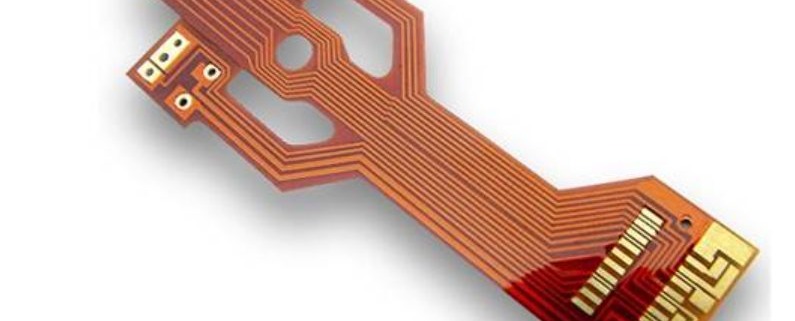
Flexible PCBs are a type of printed circuit board made from flexible materials, such as polyimide or polyester, allowing them to bend, twist, and fold without compromising electrical performance. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs built on hard substrates, flexible PCBs are designed for applications where space, weight, and movement are critical factors. In modern electronics, flexible PCB fabrication plays an essential role in industries like wearables, medical devices, and aerospace, where compactness, durability, and adaptability are required. These circuits enable devices to fit into unconventional shapes and withstand repeated mechanical stress. The flexible PCB fabrication process involves key steps such as layout design, careful material selection, trace etching, precise layering, and final testing to ensure optimal performance and reliability. With the growing demand for smaller, lighter, and more versatile electronics, flexible PCB fabrication continues to be a cornerstone technology for the next generation of innovative devices.
Flexible PCB design refers to the process of creating printed circuit boards that can bend, twist, or fold without damaging the circuitry. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, which are made from stiff materials and cannot be flexed, flexible PCBs are built using materials like polyimide, allowing for dynamic or static flexibility. The main difference lies in their construction and application—rigid PCBs are ideal for flat, stable surfaces, while flexible PCBs are perfect for compact or irregularly shaped electronic products. Flexible PCB design is commonly used in wearables, medical devices, aerospace systems, and other space-constrained electronics due to its lightweight and space-saving properties. It’s also important to understand the difference between PCB (Printed Circuit Board) and PWB (Printed Wiring Board). While often used interchangeably, PWB typically refers to boards without mounted components, whereas PCB implies a populated board.
Reference: Wevolver
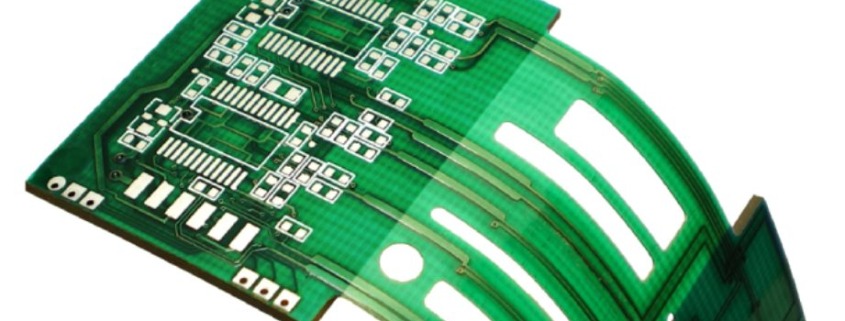
Flexible PCBs have become a cornerstone of modern electronics, enabling the development of compact, lightweight, and highly reliable devices. From wearable technology to medical devices and automotive applications, flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) offer a unique combination of flexibility, durability, and performance that rigid PCBs cannot match. The choice of flexible PCB material plays a crucial role in the design, functionality, and longevity of these circuits. The material selected affects everything from thermal resistance to mechanical flexibility and electrical performance.
In this article, we will explore the various flexible PCB materials used in the manufacturing of these circuits, highlighting their advantages and applications. Our goal is to help you understand the significance of material selection in the design process, so you can make an informed decision on the best material for your specific needs, whether you’re designing a wearable gadget or a high-performance industrial device. 阅读更多
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the foundation of nearly every modern electronic device, enabling complex circuitry to be compactly and efficiently organized. As technology evolves, product designs demand greater flexibility, lighter weight, and more dynamic form factors—needs that traditional rigid PCBs can’t always meet. This is where flexible PCBs come into play. Designed to bend, fold, and conform to irregular shapes, they have become essential in modern applications like wearable tech, medical devices, and aerospace systems. As demand grows, so does the need to find a flexible PCB manufacturer that can deliver high-quality, reliable solutions. This article aims to guide engineers, designers, and product teams through the world of flexible PCB manufacturing. We’ll explore key considerations, the manufacturing process, and how to choose the right flexible PCB manufacturer to ensure your product’s success from prototype to production. 阅读更多
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the foundation of nearly every electronic device, serving as the core platform for mounting and connecting electronic components. While traditional rigid boards have dominated the industry for decades, the demand for more compact, lightweight, and adaptable electronics has led to the increasing use of the flexible pcb board. These boards offer unique advantages, such as the ability to bend, fold, and fit into tight spaces—making them ideal for modern devices like smartphones, medical wearables, and aerospace systems. As product designs become more intricate, the flexible pcb board has become a go-to solution for engineers aiming to balance form and functionality. To meet fast-paced development cycles, services like PCBWay now offer rapid prototyping, fast-turn PCB board production, and full PCB assembly for flexible circuits. These streamlined options help innovators quickly move from design to testing and production with greater efficiency and reliability. 阅读更多
CONTACT US
4th Floor, A3 Building, HuaFeng Industrial Park, GuanTian Village, BeiHuan Road, ShiYan Street, Bao An District, Shenzhen City, Guangdong Province, China
Tel:086 (0)755-8524-1496
WhatsApp: 8615014077679
Skype: Henrychinasz
📧 pcb@alcantapcb.com
CONTACT US
SHIPPING
![]()
CERTIFCATION
![]()
recent articles
 Copper Core PCB vs Aluminium Core PCB Explained2025-09-18 - 7:13 上午
Copper Core PCB vs Aluminium Core PCB Explained2025-09-18 - 7:13 上午 Microwave PCB Manufacturers | RF Design and Fabrication2025-09-16 - 7:58 上午
Microwave PCB Manufacturers | RF Design and Fabrication2025-09-16 - 7:58 上午 Flex PCB Manufacturing Process: Step-by-Step Guide2025-09-10 - 6:59 上午
Flex PCB Manufacturing Process: Step-by-Step Guide2025-09-10 - 6:59 上午 PCB Lamination Process & Sequential Lamination2025-09-04 - 8:10 上午
PCB Lamination Process & Sequential Lamination2025-09-04 - 8:10 上午