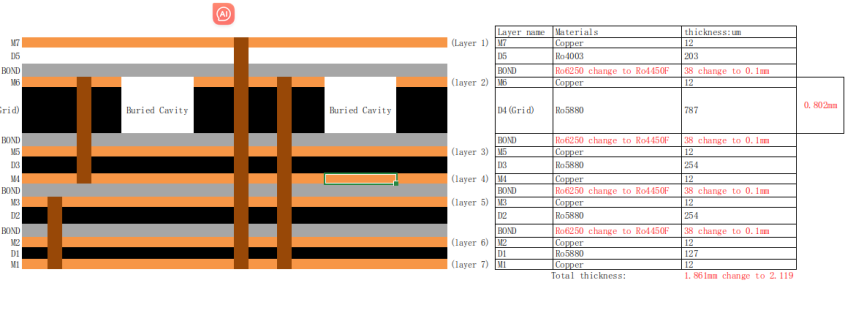
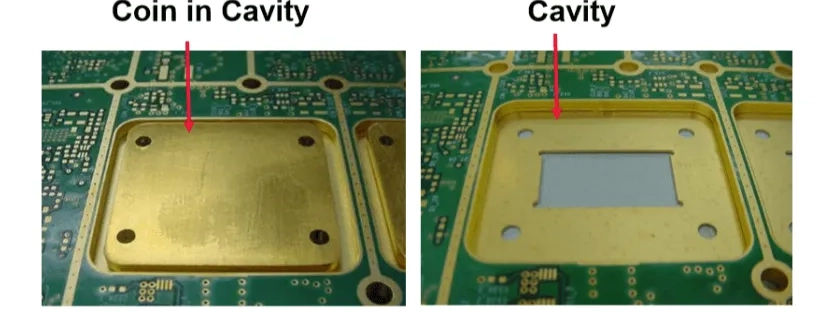
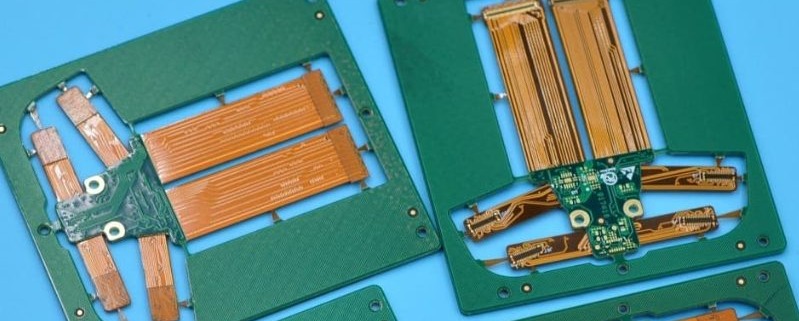
HDI PCB technology, or High-Density Interconnect PCB technology, refers to a type of printed circuit board with a higher wiring density per unit area compared to conventional PCBs. It utilizes advanced design features such as laser-drilled microvias, blind and buried vias, and high-performance thin materials to achieve superior electrical performance and space efficiency.
The importance of high-density interconnect technology in modern electronics is significant, as it enables the development of compact, lightweight, and high-performance devices. This technology is widely used in smartphones, tablets, medical devices, aerospace systems, and automotive electronics, where miniaturization and reliability are crucial. By reducing signal loss and improving power distribution, it enhances device efficiency and functionality. As the demand for smaller and more powerful electronic products grows, this technology continues to be a key enabler of innovation in the electronics industry.