Understanding the Applications of Rogers 4003C Substrate
Rogers substrates play a crucial role in the realm of high-frequency and microwave applications, providing excellent performance and reliability. Among these materials, the Rogers 4003C substrate stands out due to its unique properties, such as a low dielectric constant and minimal loss at high frequencies. This makes it an ideal choice for various electronic applications, including RF circuit boards, telecommunications, and aerospace technologies. The ability of Rogers 4003C to maintain signal integrity while minimizing signal degradation ensures its widespread use in advanced electronic designs. As industries continue to push the boundaries of technology, the demand for high-performance materials like the Rogers 4003C substrate is expected to grow, reinforcing its significance in the electronics sector. Understanding the features and applications of this material is essential for engineers and designers looking to optimize their high-frequency designs.
What is Rogers RO4003C Substrate?
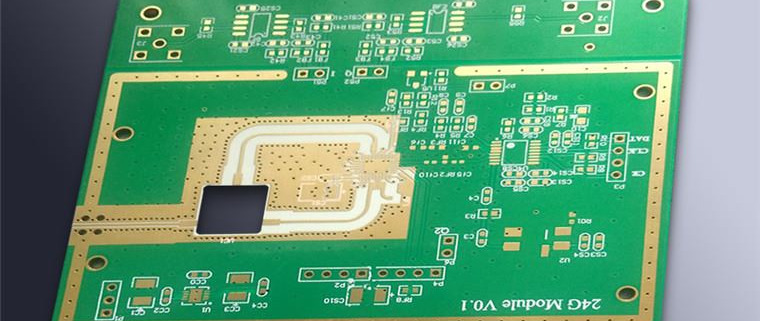
The Rogers RO4003C substrate is a high-performance laminate specifically designed for use in high-frequency applications, such as RF and microwave circuits. It is known for its low dielectric constant of approximately 3.38, which helps reduce signal loss and ensures high-speed signal transmission. This makes the Rogers RO4003C substrate ideal for applications that demand precision, such as in telecommunications, aerospace, and high-speed digital circuits.
The key characteristics of the Rogers RO4003C substrate include a low dissipation factor, which allows for efficient power transmission with minimal energy loss. It also provides excellent thermal and dimensional stability, making it suitable for environments that experience temperature fluctuations or mechanical stress.
The Rogers RO4003C substrate is composed of a unique blend of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and woven glass fabric. This combination ensures both mechanical strength and consistent electrical performance. During the manufacturing process, these components are laminated together using a specialized process that guarantees uniform thickness and surface flatness, which are critical for ensuring optimal signal integrity in high-frequency applications.
This substrate is available in a range of thickness options, providing flexibility for engineers to tailor their designs according to specific performance requirements. Its combination of electrical properties and mechanical reliability makes it a trusted choice in many high-frequency and high-speed electronic applications.
Overview of Rogers Substrate Materials
Rogers Corporation, founded in 1832, is a leader in high-performance materials for various industries, including electronics, aerospace, and telecommunications. Known for its innovative solutions, Rogers specializes in developing advanced substrates that enhance the performance of electronic devices. The company focuses on providing materials that meet the demanding requirements of high-frequency and high-speed applications, solidifying its reputation as a trusted partner in the industry.
Rogers offers a range of substrate materials tailored to different applications. Among them, the RO4350B substrate is widely recognized for its excellent thermal stability and low dielectric loss, making it suitable for microwave circuits and RF applications. With a dielectric constant of about 3.48, it provides optimal signal integrity.
Another popular substrate is RO3003, known for its good thermal conductivity and mechanical properties. It is often used in multilayer circuit designs and is favored for applications requiring a balance between performance and cost.
Each of these substrates, including the Rogers RO4003C substrate, is designed to address specific challenges in the electronics industry, ensuring that engineers have access to the right materials for their high-frequency design needs.
Thickness of RO4003
The thickness of Rogers 4003C substrates is a critical factor that influences their performance in high-frequency applications. Common thickness options for Rogers 4003C typically range from 0.008 inches (0.2 mm) to 0.062 inches (1.57 mm), allowing designers to choose the appropriate thickness based on their specific application requirements. This range offers flexibility in design, enabling the creation of both thin and thicker circuit boards tailored to different performance needs.
The impact of thickness on performance is significant. Thicker substrates generally provide better mechanical stability and heat dissipation, which is essential for high-power applications. Additionally, the thickness can affect the dielectric performance, including the propagation delay and impedance characteristics of the circuit. Thinner substrates, while offering benefits like reduced weight and lower material costs, may exhibit higher signal loss and reduced thermal management capabilities. Therefore, selecting the right thickness for the Rogers RO4003C substrate is essential to optimize the overall performance and reliability of the electronic device, ensuring that it meets the necessary specifications for high-frequency signal integrity.
Differences Between Rogers 4003C and RO4350B
When comparing Rogers 4003C and RO4350B, it is essential to examine their material composition and characteristics, as these factors directly influence their performance in various applications. The Rogers 4003C substrate features a blend of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and woven glass fabric, which contributes to its low dielectric constant of approximately 3.38 and low dissipation factor. This composition makes it particularly suitable for high-frequency applications where minimal signal loss is crucial.
In contrast, the RO4350B substrate is known for its unique blend of thermoset resin and ceramic materials, resulting in a dielectric constant of around 3.48. This composition enhances thermal stability and provides a higher thermal conductivity, making it advantageous in environments with significant thermal variation.
These differences in composition lead to variations in suitable applications. The Rogers 4003C substrate is often preferred for RF and microwave circuits that require high-performance signal integrity and efficiency. It is ideal for applications such as antenna designs and high-speed digital circuits. On the other hand, the RO4350B substrate is commonly used in applications that demand thermal stability, such as power amplifiers and high-frequency circuit designs, where the substrate’s ability to withstand heat is critical.
Overall, while both substrates serve similar markets, their distinct material properties and performance characteristics make them better suited for specific applications in the electronics industry. Understanding these differences helps engineers choose the appropriate substrate for their design needs.
Application Cases of Rogers 4003C Substrate
The Rogers 4003C substrate is widely utilized in various high-frequency circuit applications due to its superior electrical properties. One of the primary practical applications is in RF (radio frequency) circuits, where maintaining signal integrity is critical. The low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor of Rogers 4003C allow for efficient signal transmission with minimal loss, making it an excellent choice for RF amplifiers and oscillators.
In the microwave field, the Rogers 4003C substrate is frequently employed in antenna designs, such as patch antennas used in telecommunications and satellite communications. Its ability to handle high frequencies while ensuring stable performance makes it suitable for these demanding applications.
Additionally, industry case studies highlight the use of Rogers 4003C in high-speed digital circuits and wireless communication systems. For instance, leading manufacturers of mobile communication devices leverage Rogers 4003C substrates to enhance the performance of their antennas and signal processing circuits. In one case, a telecommunications company reported a significant reduction in signal loss and improved overall efficiency after transitioning to Rogers 4003C for their RF modules.
These applications demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of the Rogers 4003C substrate in high-frequency environments, underscoring its importance in the evolving landscape of electronics and communication technologies.
FAQs About rogers 4003c substrate
Rogers 4003C is a high-frequency laminate used in RF and microwave circuits. It has a low dielectric constant (around 3.38) and a low dissipation factor, making it ideal for high-speed signal transmission with minimal loss. It is composed of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and woven glass fabric for enhanced mechanical and thermal stability.
Rogers substrate materials are advanced laminates designed for high-frequency and high-performance applications. These substrates, like Rogers 4003C, are made from materials such as PTFE, ceramics, and woven glass fabric. They provide excellent electrical properties, low signal loss, and stability under varying thermal conditions, making them suitable for RF, microwave, and high-speed digital circuits.
The thickness of the Rogers 4003C substrate varies depending on design needs. Common thickness options range from 0.008 inches (0.2 mm) to 0.062 inches (1.57 mm), allowing flexibility for different applications.
The primary differences between Rogers 4003C and RO4350B are their material composition and electrical properties. Rogers 4003C has a lower dielectric constant (3.38) and is made of PTFE and woven glass fabric, while RO4350B has a higher dielectric constant (3.48) and is made of a thermoset resin combined with ceramic. RO4350B offers better thermal conductivity and is often used in applications requiring greater thermal stability.