Why Choose PCB Aluminium Substrate for LED Applications?
The pcb aluminium substrate is a type of metal-based circuit board that utilizes aluminium as its core material. Unlike traditional PCBs that use FR4 or other non-metallic materials, the aluminium substrate offers superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength. The primary purpose of using a pcb aluminium substrate is to enhance heat dissipation in electronic components that generate significant heat during operation. This substrate type is particularly useful in applications where maintaining low operating temperatures is critical to prevent damage and ensure longevity.
In the electronics industry, pcb aluminium substrates are commonly found in high-power LED lighting systems, power converters, and automotive electronics, where heat management is a key consideration. By providing efficient thermal conductivity, the aluminium substrate helps protect sensitive components, allowing for higher performance and increased durability. Its ability to handle higher temperatures makes it a preferred choice for many engineers designing heat-sensitive or high-power electronic devices.
Main Uses of PCB Aluminium Substrate
LED Lighting: One of the most prominent applications of the pcb aluminium substrate is in LED lighting systems. LED components generate significant heat during operation, and without proper heat dissipation, their efficiency and lifespan can be drastically reduced. The high thermal conductivity of the pcb aluminium substrate helps to transfer heat away from the LEDs, ensuring stable performance. Aluminium substrates allow the LEDs to function at lower temperatures, which not only improves energy efficiency but also extends the operational life of the lighting system. This is why pcb aluminium substrates are widely used in LED panels, street lights, and automotive headlights, where heat management is crucial for reliability.
Power Modules and Power Electronics: In power modules and high-power electronic devices, such as power converters and amplifiers, heat management is a major concern. The pcb aluminium substrate offers an effective solution by allowing efficient heat dissipation. As these power devices generate heat during operation, the aluminium substrate rapidly conducts the heat away from the components, preventing overheating. This ensures stable operation, enhances durability, and reduces the risk of thermal damage. These qualities make pcb aluminium substrates ideal for industrial power electronics, renewable energy systems, and other high-power applications.
Factors Affecting PCB Aluminium Substrate Price
Material Costs: One of the primary factors influencing the price of a pcb aluminium substrate is the cost of the raw materials. Aluminium is generally more affordable than other metals, but fluctuations in global aluminium prices can impact the overall cost of the substrate. Additionally, the thickness of the copper layer used in the PCB construction significantly affects pricing. A thicker copper layer improves the board’s conductivity and durability, but it also raises material costs. Thus, the final price of a pcb aluminium substrate will vary depending on the type and thickness of aluminium and copper used.
Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing techniques employed by different suppliers can lead to variations in pricing. Some manufacturers use more advanced or precise processes that improve the substrate’s quality, thermal performance, or durability. These enhanced processes may include better etching techniques or high-precision lamination, which can increase production costs. Suppliers with cutting-edge technology or strict quality control will generally charge more for pcb aluminium substrates. However, these higher costs often translate to better performance and reliability, especially in critical applications like power electronics or LED lighting.
Order Volume: The volume of the order also plays a significant role in determining the price of pcb aluminium substrates. Bulk orders tend to benefit from economies of scale, reducing the per-unit cost as production increases. Large-scale manufacturers can spread their fixed costs over a larger quantity, allowing them to offer more competitive pricing for high-volume orders. In contrast, smaller or custom orders may incur higher production costs, leading to a higher price per unit. For companies needing a large number of substrates for mass production, bulk purchasing is a cost-effective strategy.

Comparison Between Aluminium PCB and FR4
Thermal Performance: One of the most significant differences between a pcb aluminium substrate and FR4 lies in their thermal performance. Aluminium PCBs are specifically designed to offer superior heat dissipation, making them highly effective in applications where thermal management is critical. The aluminium core allows for efficient heat transfer away from sensitive electronic components, which reduces the risk of overheating and prolongs the lifespan of the device. In contrast, FR4, which is made from woven glass and epoxy resin, has limited thermal conductivity. While FR4 is suitable for low-power applications, it struggles in high-power environments where excessive heat can damage components.
Strength and Weight: Another key distinction between aluminium and FR4 is their strength and weight. Pcb aluminium substrates are known for their combination of lightness and durability. Aluminium is not only lighter than FR4 but also stronger, offering increased mechanical stability and resilience. This makes aluminium PCBs more suitable for applications that require robust physical strength, such as automotive and industrial electronics, where the boards may be exposed to harsh conditions. On the other hand, FR4 is heavier and less durable, but it remains a reliable and cost-effective option for standard electronic applications where strength is not a critical factor.
Different Applications: The choice between pcb aluminium substrate and FR4 largely depends on the specific application. FR4 is widely used in conventional electronics such as consumer gadgets, telecommunications, and general-purpose circuits, as it is cost-effective and sufficient for low-heat, low-power operations. However, pcb aluminium substrates are the go-to option for high-temperature and high-power environments. They are particularly prevalent in LED lighting, power electronics, and automotive systems where efficient heat dissipation is essential for maintaining performance and preventing component failure. Thus, while FR4 excels in standard applications, aluminium PCBs shine in more demanding thermal and mechanical conditions.
Aluminium PCB Board for LED Applications
Detailed Role in Heat Dissipation and Lifespan: In LED lighting systems, efficient heat management is critical for maintaining performance and longevity, making the pcb aluminium substrate a preferred choice. LEDs generate a significant amount of heat during operation, and if not properly dissipated, this heat can degrade the LED’s efficiency and shorten its lifespan. Aluminium substrates play a crucial role by providing a direct thermal path for heat to escape from the LED components. The aluminium core has high thermal conductivity, which allows it to quickly transfer heat away from the LEDs and dissipate it into the environment. This not only keeps the LED chips cooler but also ensures that the overall system operates more reliably. By preventing overheating, the pcb aluminium substrate significantly extends the lifespan of LED products, reducing maintenance costs and improving energy efficiency.
Usage in Various LED Lighting Systems: The versatility of pcb aluminium substrates has led to their widespread use in a variety of LED lighting systems. They are commonly used in high-power LED applications where heat dissipation is critical, such as street lights, floodlights, and high-bay lights. In these systems, the aluminium substrate ensures that the LEDs maintain optimal operating temperatures, even in harsh environments. Additionally, they are utilized in LED backlighting for televisions and monitors, where maintaining low temperatures is essential to preserving image quality and preventing color degradation over time. Pcb aluminium substrates are also found in automotive LED headlights, where efficient heat management is necessary to ensure performance and safety. Their ability to handle high temperatures while remaining lightweight and durable makes aluminium PCBs indispensable in high-power, heat-sensitive LED applications.
Thermal Conductivity of Aluminium PCB
Thermal Conductivity Characteristics of Aluminium Substrates: The high thermal conductivity of the pcb aluminium substrate is one of its most important features, especially in electronic heat management. Aluminium substrates are designed to transfer heat away from electronic components more efficiently than traditional non-metallic materials like FR4. The structure typically consists of a copper layer, a dielectric insulation layer, and an aluminium base, with the aluminium core providing a direct thermal path for dissipating heat. The dielectric layer is also engineered to have high thermal conductivity, allowing heat to pass through it quickly and reach the aluminium base, where it can be further dispersed. This efficient thermal management prevents hotspots, reduces the likelihood of component failure due to overheating, and maintains consistent performance across the system. This characteristic is vital in high-power electronics, such as LED lighting and power converters, where excess heat can significantly degrade performance and reliability.
Comparison with Other Substrates: When compared to other materials like copper and FR4, pcb aluminium substrates offer distinct advantages in terms of thermal conductivity. Copper PCBs generally have better heat conduction than aluminium PCBs due to copper’s higher intrinsic thermal conductivity. However, copper is much heavier and more expensive, making it less ideal for applications where weight and cost are important factors. On the other hand, FR4, a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate, has poor thermal conductivity. While FR4 is sufficient for low-power applications, it struggles in high-heat environments, making it unsuitable for power-intensive devices where efficient heat dissipation is essential. In contrast, the pcb aluminium substrate strikes an effective balance between good thermal conductivity, cost, and lightweight properties, offering a more practical solution for a wide range of applications where heat management is critical but cost sensitivity and weight are also considerations. Thus, while copper remains unmatched in heat conduction, aluminium’s thermal efficiency, affordability, and weight make it a widely preferred option in many electronic designs.
Leading Aluminium PCB Manufacturers and Suppliers
Key Global and Local Aluminium PCB Manufacturers: The aluminium PCB market is populated by a range of manufacturers known for their quality and innovation. Globally, companies like MCL Electronics and PCBWay stand out for their advanced manufacturing capabilities and extensive product lines. MCL Electronics specializes in high-performance PCB solutions, including aluminium substrates, catering to industries such as automotive, telecommunications, and consumer electronics. PCBWay, known for its quick turnaround times and competitive pricing, serves a wide array of sectors, offering custom solutions tailored to client needs.
In addition to these global players, there are numerous local manufacturers in various regions that contribute significantly to the aluminium PCB supply chain. For instance, in Asia, companies like Viasion Technology and Andwin PCB have established strong reputations for producing high-quality aluminium PCBs. These local suppliers often leverage their regional advantages, such as lower production costs and proximity to raw material sources, to provide competitive pricing and customized services to clients.
Exporters and Suppliers: The current state of the aluminium PCB export market is robust, driven by increasing global demand for high-performance electronic components. Key exporting countries, particularly in Asia, dominate the landscape, with China being a major player in the manufacturing and export of aluminium PCBs. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of LED technology, power electronics, and automotive applications worldwide. As a result, many manufacturers are expanding their production capacities and enhancing their technological capabilities to meet international standards.
Looking ahead, several trends are expected to shape the aluminium PCB export market. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient lighting solutions and the increasing demand for electric vehicles will likely drive further innovation and investment in aluminium PCB technology. Additionally, sustainability concerns are pushing manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly practices, including recycling and reducing waste in the production process. These trends indicate a promising future for the aluminium PCB market, with opportunities for both established players and new entrants to capitalize on the expanding global demand.
Leading Aluminium PCB Manufacturers and Suppliers
Key Global and Local Aluminium PCB Manufacturers: The aluminium PCB market is populated by a range of manufacturers known for their quality and innovation. Globally, companies like MCL Electronics and PCBWay stand out for their advanced manufacturing capabilities and extensive product lines. MCL Electronics specializes in high-performance PCB solutions, including aluminium substrates, catering to industries such as automotive, telecommunications, and consumer electronics. PCBWay, known for its quick turnaround times and competitive pricing, serves a wide array of sectors, offering custom solutions tailored to client needs.
In addition to these global players, there are numerous local manufacturers in various regions that contribute significantly to the aluminium PCB supply chain. For instance, in Asia, companies like Viasion Technology and Andwin PCB have established strong reputations for producing high-quality aluminium PCBs. These local suppliers often leverage their regional advantages, such as lower production costs and proximity to raw material sources, to provide competitive pricing and customized services to clients.
Exporters and Suppliers: The current state of the aluminium PCB export market is robust, driven by increasing global demand for high-performance electronic components. Key exporting countries, particularly in Asia, dominate the landscape, with China being a major player in the manufacturing and export of aluminium PCBs. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of LED technology, power electronics, and automotive applications worldwide. As a result, many manufacturers are expanding their production capacities and enhancing their technological capabilities to meet international standards.
Looking ahead, several trends are expected to shape the aluminium PCB export market. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient lighting solutions and the increasing demand for electric vehicles will likely drive further innovation and investment in aluminium PCB technology. Additionally, sustainability concerns are pushing manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly practices, including recycling and reducing waste in the production process. These trends indicate a promising future for the aluminium PCB market, with opportunities for both established players and new entrants to capitalize on the expanding global demand.
What Is an Aluminium Base Material PCB?
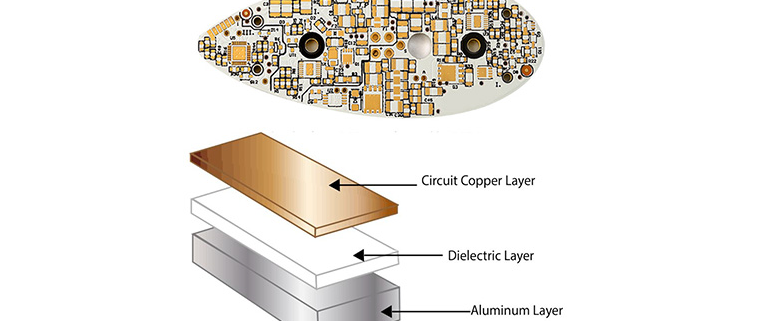
Structure of an Aluminium-Based PCB: An aluminium base material PCB, commonly referred to as an aluminium PCB, consists of several key layers that work together to provide both electrical functionality and efficient thermal management. The core structure typically includes a thick aluminium layer that serves as the substrate, a dielectric insulation layer, and a copper layer for electrical connections. The aluminium layer provides a solid foundation and excellent thermal conductivity, while the dielectric layer is designed to withstand high temperatures and ensure electrical isolation between the copper circuitry and the aluminium base. This multi-layer construction allows aluminium PCBs to effectively dissipate heat generated by electronic components, making them particularly suitable for high-power and high-temperature applications such as LED lighting, power amplifiers, and automotive electronics.
Role in High-Power, High-Temperature Applications: The unique structure of aluminium-based PCBs enables them to perform exceptionally well in environments where heat management is critical. In high-power applications, components generate significant heat during operation, which can lead to performance degradation or failure if not properly managed. Aluminium PCBs are engineered to transfer heat away from these components quickly and efficiently, preventing hotspots and ensuring reliable operation. This capability is especially important in applications such as LED lighting systems, where prolonged exposure to high temperatures can reduce efficiency and lifespan. By maintaining optimal operating temperatures, aluminium PCBs help enhance the durability and performance of electronic devices.
Why Use Aluminium in PCB?: The choice of aluminium as a base material in PCB manufacturing is driven by its exceptional properties that cater to the needs of modern electronic applications. One of the most significant advantages of aluminium is its superior heat dissipation capability. Aluminium has a high thermal conductivity, allowing it to conduct and disperse heat much more effectively than traditional materials like FR4. This property is crucial for preventing overheating in high-power applications, thereby extending the lifespan of the electronic components.
Additionally, aluminium offers substantial mechanical strength, making it a robust choice for applications that may be exposed to physical stress or harsh environmental conditions. Its lightweight nature contributes to overall device portability and efficiency, as it does not add unnecessary weight to the final product. These characteristics make aluminium an ideal material for PCB manufacturing, particularly in industries that demand high reliability and performance under thermal and mechanical stress. As a result, aluminium-based PCBs are increasingly favored in various sectors, including automotive, telecommunications, and consumer electronics, where efficient heat management and durability are paramount.
What Is the Best Substrate for PCB?
Selection of Substrates Based on Different Applications and Needs: The choice of substrate material for printed circuit boards (PCBs) is critical and largely depends on the specific requirements of the application. Different substrates offer varying electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties, making them suitable for distinct uses. For instance, standard applications such as consumer electronics or basic circuit boards often utilize FR4, a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate known for its good electrical insulation and cost-effectiveness. However, FR4 struggles in high-temperature or high-power environments due to its limited thermal conductivity.
In contrast, applications requiring efficient heat management, such as LED lighting, power electronics, or automotive systems, benefit significantly from aluminium PCBs. These substrates excel in thermal conductivity, ensuring effective heat dissipation and preventing component overheating. Additionally, high-frequency applications, such as RF circuits or microwave devices, often require materials with low dielectric loss, leading to the use of materials like Rogers or Teflon-based substrates, which provide better performance at higher frequencies.
Recommended PCB Substrate for Various Scenarios:
- General-Purpose Applications: For most consumer electronics, FR4 is the best substrate due to its balance of performance and cost. It provides adequate mechanical strength and electrical insulation for low-power applications.
- LED Lighting: For LED applications, pcb aluminium substrates are recommended. Their superior thermal conductivity helps dissipate heat effectively, prolonging the lifespan of LEDs and maintaining optimal performance.
- Power Electronics: In power modules and converters, aluminium PCBs are again the best choice due to their ability to manage heat in high-power environments. They ensure stable operation and enhance the reliability of electronic devices.
- High-Frequency Applications: For RF and microwave circuits, substrates made from materials like Rogers or Teflon are ideal. These materials offer low dielectric loss and stable performance at high frequencies, making them suitable for telecommunications and other high-frequency applications.
- Harsh Environments: For applications exposed to extreme conditions, such as automotive or aerospace systems, high-temperature substrates or ceramics may be the best choice. These materials can withstand higher thermal stresses and offer excellent mechanical strength.
The best substrate for a PCB ultimately depends on the specific application requirements, including thermal performance, frequency characteristics, and environmental conditions. By carefully selecting the appropriate substrate, engineers can optimize the performance, reliability, and longevity of their electronic devices.
FAQs About pcb aluminium substrate
An aluminum base material PCB, often referred to as an aluminum PCB, is a type of printed circuit board that utilizes aluminum as its substrate. This structure typically consists of a metal core (aluminum), a dielectric insulation layer, and a copper layer for electrical connections. The aluminum substrate is designed to provide excellent thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications that generate significant heat, such as LED lighting and power electronics.
Aluminum is used in PCBs primarily for its superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength. The ability to dissipate heat effectively helps prevent overheating of electronic components, enhancing performance and prolonging lifespan. Additionally, aluminum’s lightweight nature makes it an excellent choice for portable devices, while its durability ensures reliable operation in harsh environments.
An aluminum substrate refers to the aluminum layer used in the construction of aluminum PCBs. It serves as the core material that provides structural integrity and thermal management properties. The aluminum substrate typically includes a dielectric layer for electrical insulation and a copper layer for circuit pathways, combining to create a robust platform for electronic components.
The best substrate for a PCB depends on the specific application and requirements. For general-purpose applications, FR4 is commonly used due to its cost-effectiveness and adequate performance. However, for applications needing superior heat management, such as LED systems and power electronics, aluminum PCBs are preferred. High-frequency applications may benefit from specialized materials like Rogers or Teflon, which provide low dielectric loss and stability. Ultimately, the choice of substrate should align with the thermal, electrical, and mechanical needs of the intended application.