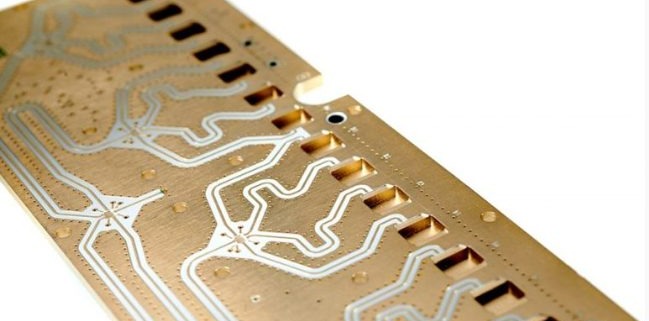
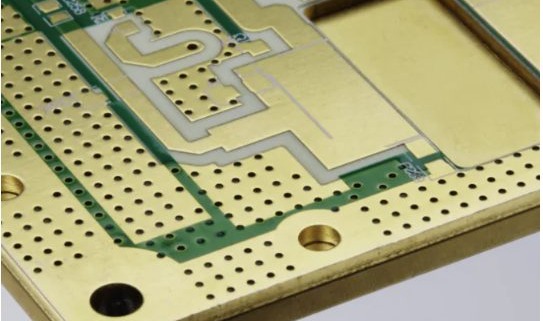
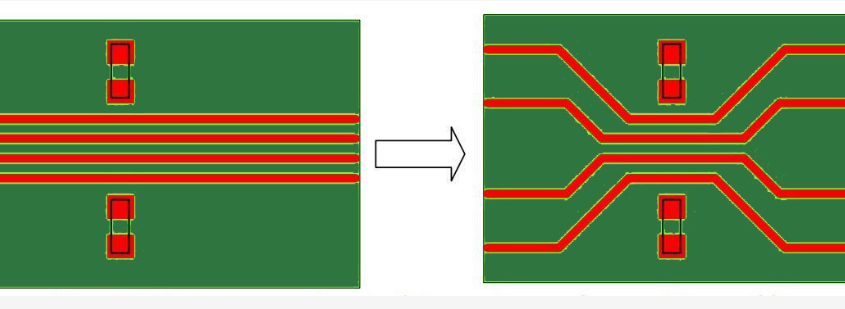
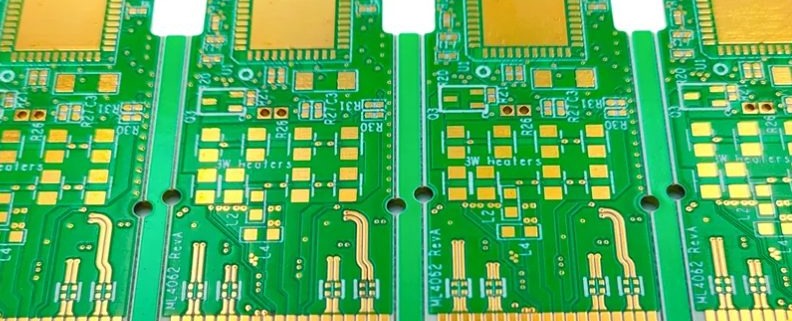
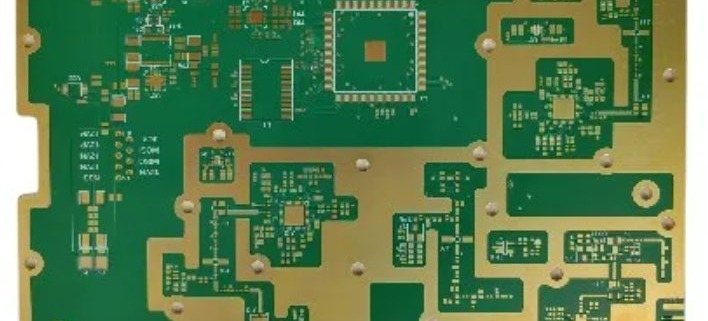
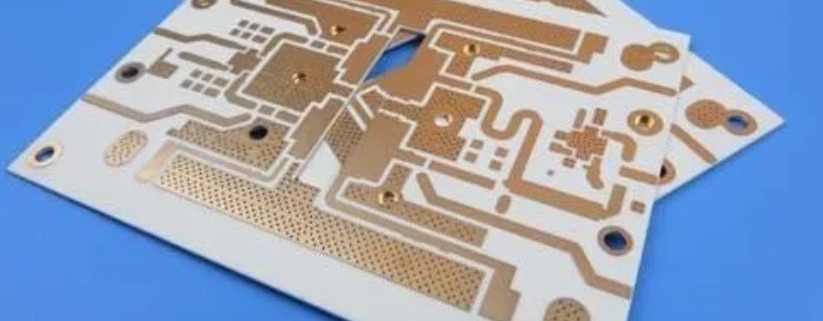
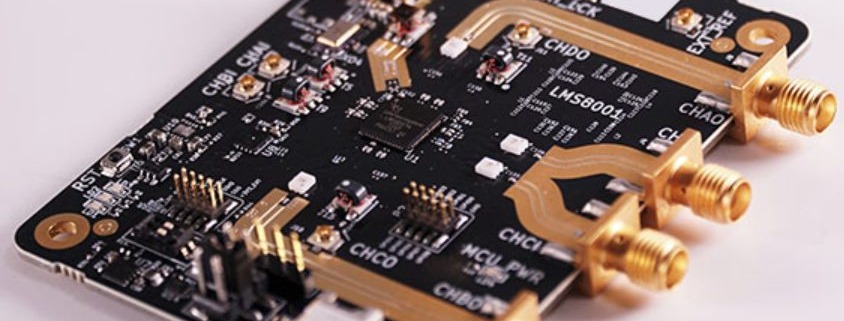
A High Frequency PCB is a specialized printed circuit board designed to operate efficiently at frequencies typically above 500 MHz, often used in RF and microwave applications. As modern electronics continue to push the boundaries of speed and performance, high frequency pcb layout has become critical in ensuring signal integrity, reliability, and overall functionality. Devices in sectors like 5G communication, automotive radar, aerospace, satellite systems, and IoT heavily rely on precise high-speed signal transmission, which demands advanced PCB layout techniques. However, designing for high frequencies introduces significant challenges. Engineers must address issues such as signal loss, electromagnetic interference (EMI), dielectric loss, and controlled impedance. A well-executed high frequency pcb layout not only minimizes these problems but also ensures consistent performance in compact, high-density environments. With the increasing demand for faster and more reliable electronic systems, mastering the principles of high frequency pcb layout is more important than ever. 阅读更多
In today’s rapidly evolving electronics landscape, high-frequency PCBs are essential components in advanced technologies such as 5G infrastructure, radar systems, RF communication devices, satellite modules, and modern automotive electronics. These applications demand fast signal transmission, low loss, and excellent impedance control—performance levels that standard FR4 materials struggle to deliver. FR4, while cost-effective and widely used, suffers from high dielectric loss and inconsistent dielectric constants at frequencies above 1 GHz, leading to signal degradation and reliability issues. This is where high frequency PCB laminates become critical. These specialized materials are engineered to maintain signal integrity at high frequencies through controlled dielectric properties and superior thermal stability. The purpose of this guide is to help engineers and designers understand what high frequency PCB laminates are, why they matter, how to select the right laminate for their application, and the key design considerations that ensure optimal performance in high-frequency environments. 阅读更多
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) technology is at the heart of modern electronics, providing the necessary platform for electrical connections in a wide variety of devices. A high-frequency laminate PCB board is a specialized type of PCB designed to operate effectively at frequencies above 500 MHz, where signal integrity becomes a critical concern. These high-frequency boards are essential for applications where performance at high speeds is a necessity. In industries like telecommunications, aerospace, automotive, and RF (Radio Frequency) systems, high-frequency PCBs are integral to ensuring reliable signal transmission, minimal loss, and reduced interference. From satellite communication systems to high-speed automotive radar and 5G networks, high-frequency laminate PCB boards enable these technologies to function efficiently at the cutting edge. The demand for high-frequency PCBs continues to grow as electronics evolve towards faster, more reliable, and higher-performance systems across diverse industries. 阅读更多
With the rapid advancement of modern electronics, the demand for high-speed, high-frequency PCBs has grown significantly. Devices in industries such as 5G telecommunications, aerospace, radar systems, automotive electronics, and RF communication rely heavily on reliable signal transmission and minimal electromagnetic interference. As a result, engineers must now pay close attention to pcb design rules for high frequency to ensure performance, stability, and compliance.
While high-speed and high-frequency PCBs often overlap in application and design approaches, they are not identical. High-speed PCBs typically focus on fast data transmission rates, while high-frequency PCBs are more concerned with the signal’s operating frequency, especially in the RF and microwave ranges. Nonetheless, both require strict layout considerations, controlled impedance, and careful material selection. Understanding the fundamental differences—and the shared design challenges—is key to creating robust and reliable products that meet today’s performance standards. 阅读更多
A High-Frequency PCB (HF PCB) is a type of printed circuit board designed to operate at frequencies typically above 1 GHz, making it essential for applications in telecommunications, aerospace, automotive, and other high-tech industries. These PCBs are crucial for ensuring optimal signal integrity and minimal loss in RF (Radio Frequency) circuits. In today’s world of advanced electronics, high-speed data transmission and efficient signal processing are vital, making high-frequency PCB materials a key consideration for performance.
The selection of the right material plays a pivotal role in the efficiency and reliability of a high-frequency PCB. Different materials have distinct properties that impact factors like signal loss, impedance, and thermal management. Choosing the correct high-frequency PCB material ensures low signal degradation and minimizes interference, thereby enhancing overall system performance. Therefore, understanding the materials suited for HF PCBs is essential for successful design and functionality in high-performance electronic devices. 阅读更多
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are fundamental to modern electronics, serving as the backbone for connecting and supporting electronic components. As technology advances, the demand for high-performance circuits has grown, especially in high-frequency applications such as 5G networks, radar systems, satellites, and other RF technologies. High-frequency PCB manufacturing plays a critical role in meeting the stringent requirements of these applications. These specialized PCBs are designed to minimize signal loss, interference, and degradation at high speeds, ensuring reliable and efficient performance. With the rise of high-speed communications and advanced radar technologies, high-frequency PCBs are essential for supporting innovations in telecommunications, aerospace, and automotive industries. The need for precise materials, optimized design, and advanced manufacturing techniques has made specialized PCB manufacturing for high-frequency circuits a key focus in modern electronics development.
阅读更多
High-frequency PCB design refers to the process of creating printed circuit boards for circuits that operate at frequencies above 1 GHz, critical in applications such as RF (Radio Frequency), wireless communication, and signal processing. These PCBs are essential for devices that require fast signal transmission and high-speed data processing, ensuring minimal signal loss and interference. The importance of high-frequency PCBs lies in their ability to handle complex, high-speed signals efficiently, as seen in smartphones, wireless routers, and radar systems. However, designing these PCBs presents several challenges, including managing electromagnetic interference (EMI), minimizing signal degradation, and controlling thermal dissipation. Following high frequency PCB design guidelines is crucial to address these issues, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in modern electronic systems.
A High-Frequency PCB refers to a type of printed circuit board specifically designed to handle high-frequency signals, typically above 1 GHz. These PCBs are crucial for applications involving radio frequency (RF) signals, including wireless communication, radar systems, and advanced medical devices.
What makes a PCB “high-frequency” is its ability to efficiently transmit high-speed signals with minimal signal loss and distortion. Unlike standard PCBs, high-frequency PCBs are built using specialized materials, such as low-loss dielectrics, which minimize attenuation and ensure signal integrity at elevated frequencies. Key characteristics that differentiate high-frequency PCBs from standard ones include their material composition, precise trace designs, and careful attention to factors like impedance control, dielectric constant, and thermal management. These factors are critical for maintaining performance in environments with high-frequency RF signals, where even the smallest variations can lead to significant signal degradation. 阅读更多
High-frequency PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) are specialized circuit boards designed to operate at frequencies typically above 1 GHz, built with materials and techniques that minimize signal loss, interference, and distortion. These boards are characterized by low dielectric loss, excellent signal integrity, and precise impedance control, making them essential for high-speed, high-performance applications. In modern communication technologies, high-frequency PCBs play a critical role in supporting fast, reliable data transmission. They are integral to wireless communication, satellite systems, radar, and 5G networks, where maintaining signal quality is crucial. High-frequency PCB communication circuits are vital in ensuring these systems operate efficiently, as even slight signal degradation can lead to performance issues. Therefore, the design and manufacture of high-frequency PCBs are essential for achieving the high data rates and low latency required in today’s advanced communication networks.
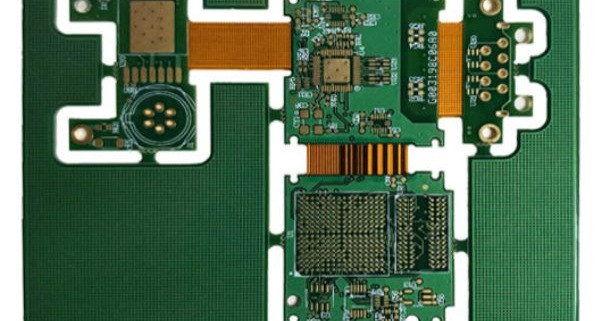
HDI Rigid-Flex PCB is a cutting-edge technology that combines the benefits of High-Density Interconnect (HDI) and Rigid-Flex PCB designs. HDI (High-Density Interconnect) refers to a PCB design technique that enables the creation of high-density, fine-pitch interconnections. This technology enhances the capacity for smaller, more intricate designs with greater functionality. On the other hand, Rigid-Flex PCB is a hybrid design that integrates both rigid and flexible substrates into one circuit board. This unique structure allows for the combination of the durability of rigid boards with the flexibility of flexible boards, enabling more complex and compact designs.
When HDI Rigid-Flex PCB is used, the result is a high-performance, compact solution that is ideal for applications where space and reliability are crucial, such as in consumer electronics, medical devices, and aerospace technologies. By merging HDI’s dense interconnection capabilities with the adaptable nature of Rigid-Flex boards, this technology delivers unparalleled design flexibility and performance efficiency. 阅读更多
CONTACT US
4th Floor, A3 Building, HuaFeng Industrial Park, GuanTian Village, BeiHuan Road, ShiYan Street, Bao An District, Shenzhen City, Guangdong Province, China
Tel:086 (0)755-8524-1496
WhatsApp: 8615014077679
Skype: Henrychinasz
📧 pcb@alcantapcb.com
CONTACT US
SHIPPING
![]()
CERTIFCATION
![]()
recent articles
 Copper Core PCB vs Aluminium Core PCB Explained2025-09-18 - 7:13 上午
Copper Core PCB vs Aluminium Core PCB Explained2025-09-18 - 7:13 上午 Microwave PCB Manufacturers | RF Design and Fabrication2025-09-16 - 7:58 上午
Microwave PCB Manufacturers | RF Design and Fabrication2025-09-16 - 7:58 上午 Flex PCB Manufacturing Process: Step-by-Step Guide2025-09-10 - 6:59 上午
Flex PCB Manufacturing Process: Step-by-Step Guide2025-09-10 - 6:59 上午 PCB Lamination Process & Sequential Lamination2025-09-04 - 8:10 上午
PCB Lamination Process & Sequential Lamination2025-09-04 - 8:10 上午