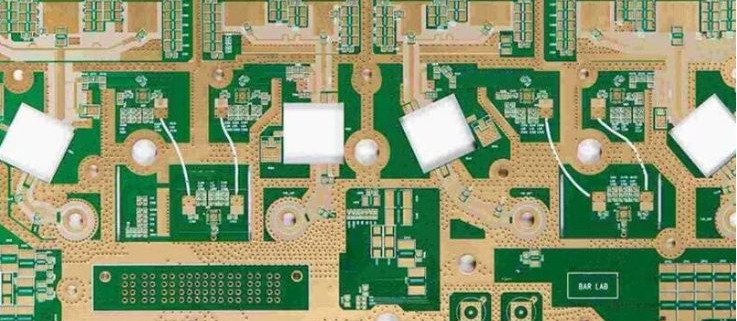
Key Benefits of Rogers PCB Substrates for High-Frequency Designs
Rogers PCB materials are a key component in advanced printed circuit board (PCB) technology, renowned for their superior performance in high-frequency and high-speed applications. Manufactured by Rogers Corporation, these materials are designed to address the challenges of signal integrity and thermal management, making them ideal for use in microwave, RF, and other high-frequency circuits.
The importance of Rogers materials in PCB manufacturing lies in their exceptional electrical properties, such as low dielectric loss and stable dielectric constant, which are crucial for maintaining signal quality and minimizing interference. Unlike conventional FR4 materials, Rogers substrates provide enhanced performance at high frequencies, offering better thermal stability and mechanical strength. This makes them essential for applications requiring reliable and efficient signal transmission, such as telecommunications, aerospace, and automotive electronics. Their advanced characteristics help engineers meet the demanding requirements of modern electronic designs, ensuring robust and efficient circuit performance.
Overview of Rogers PCB Substrate
What is Rogers Material?
Rogers PCB substrates are advanced materials designed to enhance the performance of printed circuit boards (PCBs) in high-frequency and high-speed applications. Produced by Rogers Corporation, a leading innovator in advanced material solutions, these substrates are engineered to meet the stringent demands of modern electronic systems. Rogers materials are known for their superior electrical properties, making them a popular choice for high-performance PCBs used in telecommunications, aerospace, and other high-tech industries.
Characteristics of Rogers Substrate
High-Frequency Performance: Rogers PCB substrates are renowned for their excellent high-frequency performance. This is primarily due to their low dielectric loss and stable dielectric constant, which minimize signal attenuation and distortion. These properties are crucial for maintaining signal integrity in applications such as RF (radio frequency) and microwave circuits, where precise signal transmission is essential.
Thermal Stability: Another key characteristic of Rogers substrates is their exceptional thermal stability. These materials are designed to withstand high temperatures without significant degradation in performance. This makes them suitable for applications where heat dissipation is a concern, such as in high-power electronics or environments with fluctuating temperatures. Rogers substrates can maintain their electrical properties and mechanical integrity even under thermal stress.
Mechanical Strength: Rogers PCB substrates also offer notable mechanical strength. They are engineered to provide robust structural support for the electronic components mounted on them. This strength ensures that the PCB can withstand physical stresses during manufacturing and operation, contributing to the overall durability and reliability of the final electronic product. This mechanical resilience is particularly important in demanding environments where PCBs are subjected to vibrations, shocks, or other physical challenges.
In summary, Rogers PCB substrates stand out due to their superior high-frequency performance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength, making them a valuable choice for high-performance and high-reliability electronic applications.
Different Types of Rogers PCB Substrate
Rogers 5880 Substrate
Key Features: The Rogers 5880 substrate is designed for high-frequency applications, offering excellent electrical performance with low dielectric loss and a stable dielectric constant. It features a ceramic-filled PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) composite, which enhances its thermal stability and mechanical strength. The material is known for its low moisture absorption, which helps maintain consistent performance in various environmental conditions.
Application Areas: Rogers 5880 is widely used in high-frequency applications such as microwave circuits, RF communication systems, and high-speed digital circuits. It is particularly suitable for applications that require high thermal conductivity and low signal attenuation, making it ideal for advanced telecommunications, aerospace systems, and high-power RF amplifiers.
Performance Parameters: The Rogers 5880 substrate typically has a dielectric constant (Dk) of around 2.20, which provides stable signal propagation at high frequencies. Its dissipation factor (Df) is very low, often around 0.0009, which minimizes signal loss and ensures high signal integrity. The substrate also has a thermal conductivity of about 0.7 W/mK, which aids in effective heat dissipation.
Rogers RO4350B Substrate
Key Features: The Rogers RO4350B substrate is a high-performance material featuring a woven glass-reinforced PTFE composite. This combination provides excellent electrical properties, high thermal stability, and good mechanical strength. It is known for its low dielectric loss and stable dielectric constant, making it suitable for high-frequency and high-speed applications.
Application Areas: Rogers RO4350B is used in a range of applications, including RF and microwave circuits, high-speed digital circuits, and advanced communication systems. Its properties make it particularly useful for high-frequency PCB designs in telecommunications, automotive radar systems, and satellite communication.
Performance Parameters: The Rogers RO4350B substrate has a dielectric constant (Dk) of approximately 3.48, which is higher than that of Rogers 5880 but still suitable for high-frequency applications. The material has a low dissipation factor (Df) of around 0.0037, which helps in maintaining signal integrity and reducing signal loss. Additionally, it has a thermal conductivity of about 0.6 W/mK, aiding in heat dissipation.
Both Rogers 5880 and RO4350B substrates offer distinct advantages for different high-frequency and high-speed applications, with their specific features and performance parameters tailored to meet various design requirements.
Pricing of Rogers PCB Substrate
Rogers PCB Substrate Price
Price Range: The cost of Rogers PCB substrates varies significantly depending on the specific material, thickness, and order quantity. Generally, Rogers substrates are priced higher than traditional FR4 materials due to their advanced properties and specialized manufacturing processes. For instance, Rogers 5880 and RO4350B substrates can range from $50 to $200 per square meter, depending on the supplier and specific product specifications.
Factors Affecting Price: Several factors influence the pricing of Rogers PCB substrates:
- Material Type: Different Rogers materials, such as 5880 and RO4350B, have varying costs due to their distinct compositions and performance characteristics. Materials with lower dielectric loss or higher thermal conductivity may be priced higher.
- Thickness and Size: Thicker substrates or those with larger dimensions typically cost more. Custom sizes and special configurations can also impact the price.
- Order Quantity: Bulk orders or long-term contracts often result in lower per-unit prices due to economies of scale. Smaller orders may incur higher costs.
- Supplier and Market Conditions: Prices can vary between suppliers based on their pricing strategies, supply chain factors, and market demand. Fluctuations in raw material costs and changes in production capabilities also affect pricing.
Comparison of Rogers 5880 and RO4350B Prices
Price Differences Between Materials: Rogers 5880 is generally priced higher than RO4350B due to its advanced material composition and specialized applications. The higher cost of Rogers 5880 reflects its superior performance in high-frequency applications and its enhanced thermal and mechanical properties. In contrast, Rogers RO4350B, while still a high-performance material, is often more affordable, making it a cost-effective option for many high-frequency and RF applications.
Market Trends: The pricing of Rogers PCB substrates is influenced by several market trends:
- Demand and Supply Dynamics: Increased demand for high-frequency and high-speed electronic devices drives up prices. Conversely, oversupply or advancements in manufacturing technologies can lead to price reductions.
- Raw Material Costs: Fluctuations in the cost of raw materials used in Rogers substrates, such as PTFE and glass fibers, can impact substrate prices. Changes in the cost of these materials affect overall production costs.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in substrate manufacturing and improvements in material performance can lead to cost adjustments. New technologies may either reduce production costs or introduce more expensive high-performance options.
In summary, while Rogers PCB substrates are priced higher than traditional materials, their cost is justified by their superior performance and specialized applications. Understanding the factors that influence pricing can help in making informed decisions based on specific project requirements and budget constraints.
Performance Parameters of Rogers PCB Substrate
Dielectric Constant of Rogers Materials
Definition and Significance: The dielectric constant (Dk) of Rogers PCB substrates is a critical parameter that measures the material’s ability to store electrical energy in an electric field. It is defined as the ratio of the capacitance of a capacitor with the dielectric material to the capacitance of the same capacitor with a vacuum. A higher dielectric constant indicates that the material can store more electrical energy. For Rogers materials, the dielectric constant is tailored to meet specific high-frequency performance requirements, making it crucial for ensuring stable signal propagation and maintaining the desired impedance in PCB designs.
Impact on PCB Performance: The dielectric constant of Rogers PCB substrates significantly influences PCB performance, especially in high-frequency applications. Materials with a stable and low dielectric constant, such as Rogers 5880 with a Dk of around 2.20, help in reducing signal attenuation and distortion, ensuring accurate signal transmission over long distances. Conversely, a higher dielectric constant, such as that of Rogers RO4350B at approximately 3.48, can be suitable for certain high-frequency applications where impedance control and signal integrity are still maintained. Consistency in dielectric constant across varying frequencies is essential for reliable circuit performance and minimizing signal loss.
Other Key Parameters
Dielectric Loss: Dielectric loss, represented by the dissipation factor (Df), measures the energy lost as heat when an electric field is applied to the dielectric material. For Rogers substrates, dielectric loss is kept to a minimum to ensure efficient signal transmission and reduced heat generation. For instance, Rogers 5880 has a low Df of about 0.0009, while Rogers RO4350B has a slightly higher Df of around 0.0037. Lower dielectric loss values are crucial for high-speed and high-frequency applications, as they help in maintaining signal integrity and reducing power dissipation.
Thermal Conductivity: Thermal conductivity measures a material’s ability to conduct heat. For Rogers PCB substrates, thermal conductivity is an important factor as it affects the substrate’s ability to dissipate heat generated by electronic components. Effective heat management is essential for maintaining the reliability and performance of high-power or high-frequency PCBs. Rogers substrates offer good thermal conductivity, with Rogers 5880 typically having a thermal conductivity of around 0.7 W/mK and Rogers RO4350B around 0.6 W/mK. Higher thermal conductivity helps in efficiently managing heat and preventing thermal stress on the PCB.
In summary, the dielectric constant, dielectric loss, and thermal conductivity of Rogers PCB substrates are critical parameters that determine their suitability for high-frequency and high-performance applications. Understanding these parameters helps in selecting the right material for specific PCB design requirements, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in electronic systems.
Comparison Between Rogers PCB Substrate and FR4
What is FR4?
Basic Definition and Applications: FR4 is a widely used material in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs). It is a composite of woven glass fibers and epoxy resin, providing a balance between electrical performance, thermal stability, and cost. The “FR” in FR4 stands for “Flame Retardant,” indicating its ability to resist combustion. This material is commonly used in a variety of electronic devices due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. FR4 is suitable for applications ranging from consumer electronics to industrial machinery, where moderate performance characteristics and affordability are key considerations.
Key Differences Between Rogers PCB Substrate and FR4
Frequency Performance: Rogers PCB substrates are designed to excel in high-frequency applications, offering superior performance compared to FR4. Rogers materials, such as Rogers 5880 and RO4350B, feature low dielectric loss and stable dielectric constants, which are critical for maintaining signal integrity in RF and microwave circuits. FR4, on the other hand, is less effective at high frequencies due to its higher dielectric loss and greater signal attenuation. This makes Rogers substrates the preferred choice for high-speed and high-frequency applications where precise signal transmission is essential.
Thermal Stability: Rogers PCB substrates exhibit better thermal stability compared to FR4. Rogers materials are engineered to withstand higher temperatures without significant degradation in performance. For instance, Rogers substrates can handle high thermal loads and maintain their electrical and mechanical properties under thermal stress. In contrast, FR4 has lower thermal stability and can suffer from thermal degradation or warping at elevated temperatures. This makes Rogers substrates more suitable for high-power and high-temperature environments, where efficient heat dissipation and thermal management are crucial.
Mechanical Properties: In terms of mechanical properties, Rogers PCB substrates generally offer superior strength and durability compared to FR4. Rogers materials are designed to provide robust structural support, ensuring that the PCB can withstand physical stresses during manufacturing and operation. This is particularly important in applications subject to vibrations, shocks, or mechanical stress. FR4, while providing adequate mechanical support for many applications, may not offer the same level of durability and resistance to mechanical stress as Rogers substrates.
In summary, Rogers PCB substrates offer significant advantages over FR4 in high-frequency performance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength. While FR4 remains a popular choice due to its cost-effectiveness and general suitability for many applications, Rogers materials are preferred for specialized applications requiring superior performance in high-speed and high-temperature environments.
Applications of Rogers PCB Substrate
Microwave and RF Applications
Suitability of Materials: Rogers PCB substrates are highly suitable for microwave and RF (radio frequency) applications due to their superior electrical properties. Materials like Rogers 5880 and RO4350B are specifically designed to handle the challenges of high-frequency signal transmission. Their low dielectric loss and stable dielectric constant ensure minimal signal attenuation and distortion, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity in microwave and RF circuits. Additionally, the high thermal stability of Rogers materials helps manage heat generated in high-power RF applications, preventing performance degradation and ensuring reliability.
Typical Application Examples: Rogers PCB substrates are commonly used in a range of microwave and RF applications, including:
- Aerospace and Defense: High-performance communication systems, radar systems, and satellite communications rely on Rogers substrates for their ability to operate efficiently at high frequencies and withstand harsh environmental conditions.
- Wireless Communication: Cellular base stations, Wi-Fi routers, and other wireless communication devices utilize Rogers PCBs to ensure reliable signal transmission and high-speed data transfer.
- Medical Devices: Advanced medical imaging equipment and diagnostic tools benefit from the precision and stability of Rogers materials in their RF and microwave components.
High-Frequency Electronic Devices
Suitability of Materials: Rogers PCB substrates excel in high-frequency electronic devices due to their low dielectric loss and high thermal conductivity. These properties are essential for maintaining signal quality and managing heat in devices that operate at high speeds and frequencies. The stability of Rogers materials at elevated frequencies ensures that electronic devices perform reliably and efficiently, even under demanding conditions.
Typical Application Examples: Rogers PCB substrates are used in various high-frequency electronic devices, including:
- High-Speed Digital Circuits: Advanced digital systems, such as high-speed data processors and memory modules, use Rogers materials to manage signal integrity and reduce noise in high-speed data transmission.
- Telecommunications Equipment: Routers, switches, and other telecommunications hardware use Rogers substrates to ensure stable and high-performance operation in data communication networks.
- Automotive Electronics: Modern automotive systems, including radar and sensor systems, rely on Rogers PCBs for their ability to handle high-frequency signals and operate reliably in automotive environments.
Rogers PCB substrates are highly valued for their performance in microwave and RF applications as well as high-frequency electronic devices. Their advanced properties make them ideal for a wide range of specialized applications, where reliable signal transmission, thermal management, and durability are critical.
FAQs About rogers pcb substrate
Rogers material for PCB refers to a range of high-performance substrates produced by Rogers Corporation, designed specifically for high-frequency and high-speed electronic applications. These materials, such as Rogers 5880 and RO4350B, are engineered to provide superior electrical performance with low dielectric loss, high thermal stability, and mechanical strength. Rogers PCB materials are commonly used in advanced telecommunications, aerospace, and high-speed digital circuits due to their ability to maintain signal integrity and handle high-frequency signals effectively.
A Rogers substrate is a type of printed circuit board (PCB) material manufactured by Rogers Corporation. It consists of a composite material, often combining PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) with woven glass fibers or ceramics, designed to enhance the performance of PCBs in high-frequency and high-speed applications. Rogers substrates are known for their low dielectric loss, stable dielectric constant, and high thermal conductivity, making them suitable for demanding electronic applications such as microwave circuits, RF (radio frequency) systems, and high-speed digital circuits.
The primary differences between Rogers PCB substrates and FR4 materials are:
Frequency Performance: Rogers PCBs are designed for high-frequency applications and offer superior electrical performance with lower dielectric loss and more stable dielectric constants compared to FR4. FR4 is more suitable for standard, lower-frequency applications.
Thermal Stability: Rogers substrates have higher thermal stability and can maintain performance under higher temperatures and thermal stress. FR4, while adequate for many applications, may degrade or warp under high thermal conditions.
Mechanical Properties: Rogers PCBs generally provide better mechanical strength and durability, making them suitable for environments subject to physical stress. FR4 offers good mechanical support but may not be as robust in demanding applications.
Rogers microwave materials are primarily made of a composite of PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) and ceramic fillers, or woven glass fibers combined with PTFE. These materials are designed to offer low dielectric loss, stable dielectric constant, and high thermal conductivity, which are essential for maintaining signal integrity and managing heat in microwave circuits. The specific composition of the material may vary depending on the product line and its intended application, but the focus is on providing high-performance characteristics suitable for microwave and RF applications.