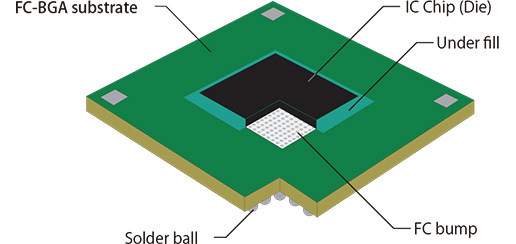
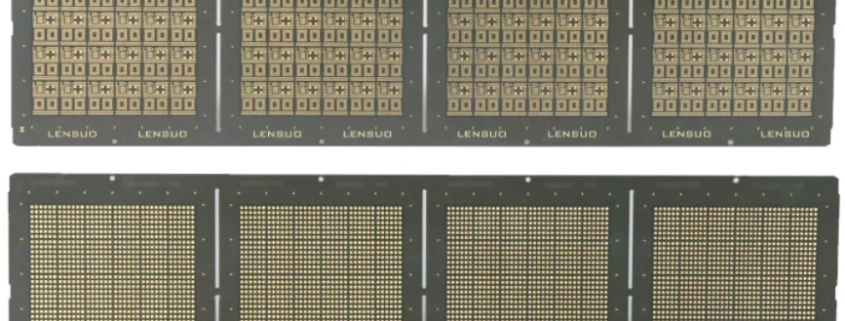
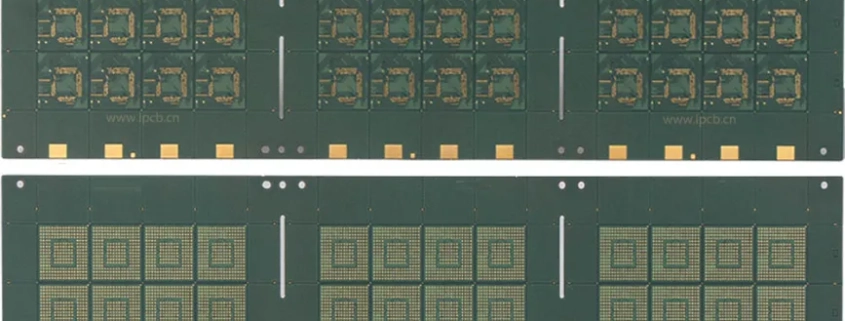
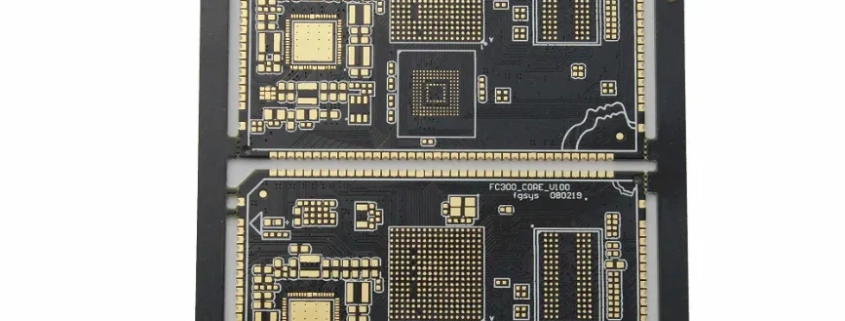
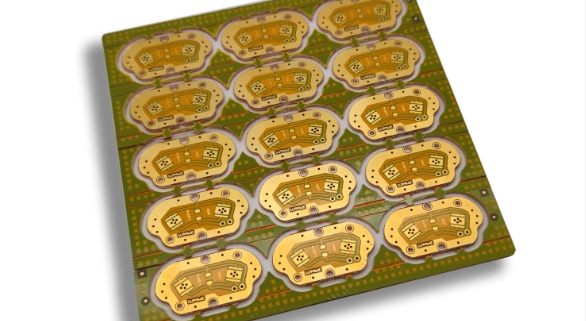
Chip substrate material, a crucial component in semiconductor technology, serves as the foundational layer upon which semiconductor devices are fabricated. This material provides mechanical support, electrical connectivity, and thermal management for integrated circuits (ICs). The substrate’s primary role is to ensure that the chip functions reliably by maintaining structural integrity and facilitating effective heat dissipation.
The importance of chip substrate material cannot be overstated. It directly influences the performance, efficiency, and longevity of electronic devices. High-quality substrates enable advanced functionalities in various applications, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery and automotive systems. As the demand for smaller, faster, and more efficient devices grows, the development and optimization of substrate materials become increasingly critical. This foundational component supports the rapid evolution of technology, making innovations in fields like artificial intelligence, telecommunications, and computing possible. The right substrate material ensures that the semiconductor devices can operate under optimal conditions, meeting the high standards required by modern electronics.
阅读更多