How to Test a PCB: Methods, Equipment, and Multimeter Guide
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics, powering everything from smartphones and computers to industrial machinery. But even the most carefully designed PCB can fail due to faulty components, poor solder joints, or damaged traces. That’s why PCB testing is critical—not just in manufacturing, but also during troubleshooting and repair.
In this article, we’ll walk through how to test a PCB with a multimeter, explore different PCB testing methods, highlight testing equipment and software, and explain how to identify faulty PCBs. Whether you’re a hobbyist repairing a circuit board or a professional engineer working on quality control, this guide will help you approach PCB testing systematically.
How to Test a PCB with Multimeter
A digital multimeter (DMM) is the most accessible and versatile tool for PCB testing. It can measure continuity, resistance, voltage, current, diodes, and in some cases capacitance. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Safety Precautions
-
Disconnect power before testing (unless you are performing live voltage measurements).
-
Discharge capacitors to avoid shocks.
-
Use anti-static wrist straps to protect sensitive components.
Visual Inspection
Before using the multimeter, look for obvious issues:
-
Burn marks, cracks, or discoloration
-
Broken or lifted solder joints
-
Bent or corroded connectors
-
Warped PCB layers
Continuity Test
-
Switch the multimeter to continuity mode.
-
Touch both probes across a trace, via, or switch contact.
-
A beep means the connection is intact; silence indicates an open circuit.
Resistance Test
-
Measure resistor values and compare them with design specifications.
-
Unexpectedly low resistance often means a short circuit.
-
Extremely high resistance may indicate a broken trace or faulty resistor.
Voltage Test (Powered On)
-
Power the PCB and set the multimeter to DC voltage.
-
Check power rails (+3.3V, +5V, +12V, etc.).
-
Confirm ICs and regulators are receiving correct voltage.
-
Abnormal voltage indicates possible short, regulator failure, or faulty capacitor.
Diode and Transistor Check
-
Use diode mode to test forward/reverse bias.
-
A reading of ~0.6–0.7 V is normal for silicon diodes in forward bias.
-
A zero or infinite reading suggests a shorted or open diode/transistor.
Capacitor Test
-
Some multimeters have a capacitance function.
-
If not, you can check for shorts by measuring resistance across capacitor terminals (should charge up, not stay at 0 Ω).
Tip: Start with simple continuity and resistance checks before powering on. This prevents additional damage if the PCB has a short.

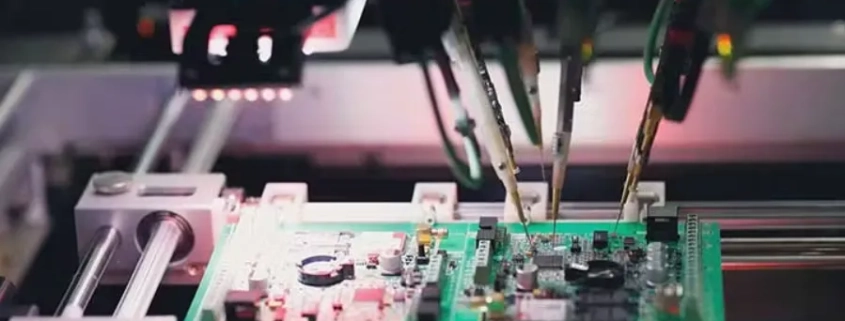
Types of PCB Testing Methods
Professional PCB testing involves more than just a multimeter. In manufacturing environments, several methods are used to ensure functionality and quality.
-
In-Circuit Testing (ICT): Uses bed-of-nails fixtures to check component values and solder connections.
-
Flying Probe Testing: Similar to ICT, but probes move dynamically instead of requiring a custom fixture.
-
Functional Circuit Test (FCT): Simulates real-world conditions to confirm the PCB works as intended.
-
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Uses cameras to detect soldering defects, missing components, or misalignment.
-
X-Ray Inspection: Ideal for detecting hidden issues in BGAs or multilayer solder joints.
-
Burn-in Testing: Stresses the PCB under high voltage/current to identify early-life failures.
Each method has trade-offs in cost, speed, and coverage. For DIY repair, a multimeter + visual inspection is usually enough, while manufacturers rely on ICT, AOI, and X-ray inspection.
Get a Quotation For How to Test a PCB Now
PCB Board Testing Equipment
The choice of equipment depends on whether you are a repair technician or a manufacturer. Common tools include:
-
Digital & Analog Multimeters – basic voltage, resistance, continuity checks.
-
Oscilloscope – observes signal integrity and timing.
-
LCR Meter – measures inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R).
-
Bench Power Supply with Current Limiting – safely powers boards for live testing.
-
ICT and Flying Probe Testers – advanced factory equipment.
-
Thermal Imaging Cameras – useful for spotting overheating components.
Get a Quotation For How to Test a PCB Now
PCB Testing Software
Software plays an increasing role in PCB testing, especially during design and simulation.
-
CAD Simulation Tools (Altium Designer, Cadence, KiCad) – test signals before fabrication.
-
Boundary Scan & JTAG Tools – allow digital testing of ICs.
-
Automated Test Pattern Generation (ATPG) – speeds up manufacturing QA.
-
Signal Integrity & Power Integrity Analysis Software – predicts real-world PCB performance.
For beginners, simulation software can help catch design flaws early, while manufacturers integrate these tools into automated test systems.
Get a Quotation For How to Test a PCB Now
How to Test PCB Keyboard
Keyboards have unique PCBs with switch matrices. Testing them requires a slightly different approach.
-
Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter in continuity mode to check each key switch pad. Pressing a key should close the circuit.
-
Matrix Trace Check: Follow the matrix traces to ensure no breaks.
-
Controller Testing: Verify that the keyboard controller IC is receiving proper power and sending signals.
-
Fault Isolation: If some keys work and others don’t, the issue may be a broken trace or a faulty diode in the switch matrix.
Get a Quotation For How to Test a PCB Now
How to Test a Faulty PCB
Sometimes the entire PCB seems dead or unstable. Here’s how to approach it:
-
Check for Physical Damage: Burn marks, broken connectors, corrosion.
-
Measure Power Rails: If there is no voltage, suspect regulators or shorts.
-
Component Testing: Resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors can all fail.
-
Compare with Known Good Board: Helps quickly identify anomalies.
-
Signal Tracing: Use oscilloscope or logic analyzer to follow signals.
If multiple components test fine but the PCB still fails, the issue could be a faulty IC, microcontroller, or an internal trace problem.
Get a Quotation For How to Test a PCB Now
PCB Testing Methods PDF and Documentation
Recording test results is as important as the testing itself. Many companies generate PCB testing PDF reports that include:
-
List of tests performed
-
Pass/fail results
-
Measured values vs expected values
-
Notes on visual inspection
Following IPC standards (such as IPC-9252 for electrical testing) ensures consistency and quality across production runs.
Get a Quotation For How to Test a PCB Now
About How to Test a PCB FAQs
Q: How do I test a PCB with a multimeter?
A: Start with continuity and resistance tests, then move on to voltage measurements and diode checks.
Q: How do you know if a PCB board is bad?
A: Signs include burn marks, no power output, incorrect voltage, or non-functional components.
Q: Can I test PCB without powering it on?
A: Yes. Use continuity and resistance checks to find shorts or opens.
Q: How to test PCB board with multimeter PDF version?
A: Many guides (including this one) can be exported as a PDF for offline use.
Q: What’s the difference between PCB testing and debugging?
A: Testing checks for compliance and functionality, while debugging finds and fixes faults.