Glass Substrate Package: Advancing Semiconductor Integration
Glass Substrate in Packaging
Role of Glass Substrate in Semiconductor Packaging
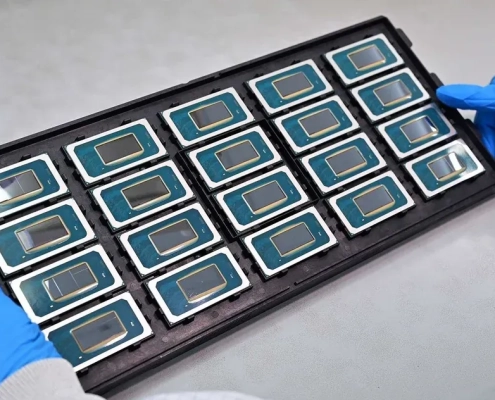
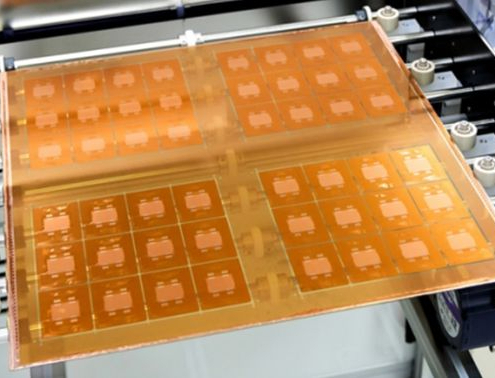
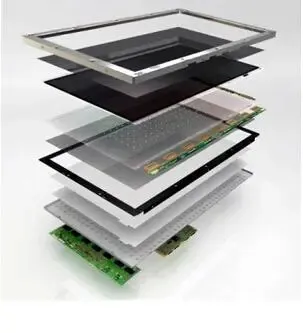
Glass substrate package plays a pivotal role in semiconductor packaging by providing a stable platform for integrating and interconnecting various electronic components. It serves as a foundation upon which semiconductor devices are built, facilitating the assembly of integrated circuits (ICs) and other electronic modules. Glass package substrates offer excellent dimensional stability, allowing for precise alignment and bonding of semiconductor chips, wire bonds, and other package elements. Moreover, they provide electrical insulation and thermal dissipation, ensuring optimal performance and reliability of the packaged semiconductor devices. In advanced packaging technologies such as System-in-Package (SiP) and 3D integration, glass substrates enable the integration of multiple chips and components in a compact and efficient manner, enhancing the functionality and miniaturization of electronic devices.
Advantages of Using Glass Substrate
- High Electrical Insulation: Glass package substrates exhibit excellent electrical insulation properties, minimizing signal interference and improving the reliability of electronic devices.
- Excellent Thermal Management: Glass substrates offer superior thermal conductivity, efficiently dissipating heat generated by semiconductor devices and ensuring stable operation under demanding conditions.
- Dimensional Stability: Glass substrate package provides exceptional dimensional stability, maintaining precise alignment and integrity of semiconductor components throughout the packaging process and the device’s lifecycle.
- Compatibility with Advanced Packaging Technologies: Glass substrates are compatible with various advanced packaging technologies such as flip-chip bonding, through-glass vias (TGVs), and wafer-level packaging, enabling the integration of complex and high-performance semiconductor devices.
- Environmental Sustainability: Glass substrates are environmentally friendly, being recyclable and chemically inert, thereby reducing the environmental impact of electronic waste.
Overall, the use of glass package substrates offers significant advantages in terms of performance, reliability, and sustainability, making them an ideal choice for advanced semiconductor packaging applications.
Considerations for Glass Substrate Package
Industry Applications of Glass Substrate Package
Intel’s Glass Substrate Package Innovations
Glass Core Substrate in Glass Substrate Package
Definition and Significance of Glass Core Substrate
A glass core substrate is a specialized type of substrate used in glass substrate packaging, characterized by a central layer of glass material surrounded by additional layers for structural support and electrical connectivity. The glass core substrate serves as the foundation for semiconductor devices, providing a stable platform for mounting and interconnecting electronic components. Its significance lies in its ability to offer excellent thermal conductivity, dimensional stability, and electrical insulation, making it an ideal choice for high-performance and reliable packaging solutions.
Applications and Benefits of Glass Core Substrate in Packaging
- High-Density Integration: Glass core substrates enable high-density integration of semiconductor components, allowing for the assembly of complex electronic systems in a compact form factor.
- Enhanced Thermal Management: The superior thermal conductivity of glass core substrates facilitates efficient heat dissipation from semiconductor devices, ensuring optimal performance and reliability even under high operating temperatures.
- Improved Signal Integrity: Glass core substrates provide excellent electrical insulation, minimizing signal interference and ensuring reliable transmission of electronic signals within the package.
- Compatibility with Advanced Packaging Techniques: Glass core substrates are compatible with various advanced packaging techniques such as flip-chip bonding, through-glass vias (TGVs), and embedded component technology, enabling the integration of multiple chips and components in a single package.
- Environmental Sustainability: Glass core substrates are environmentally friendly and recyclable, contributing to the overall sustainability of electronic devices and reducing the environmental impact of electronic waste.
Overall, the use of glass core substrates in glass substrate packaging offers numerous advantages, ranging from improved thermal management and signal integrity to enhanced integration and sustainability, making them an indispensable component in modern semiconductor packaging solutions.
Leading Glass Substrate Manufacturers
FAQs About Glass Substrate Package
What is the glass substrate?
A glass substrate is a flat, thin piece of glass used as a base for various electronic components, such as semiconductor chips. It provides structural support and serves as a foundation for building electronic devices.
What is glass core substrate?
A glass core substrate is a specialized type of glass substrate with a central layer of glass surrounded by additional layers. It’s commonly used in semiconductor packaging, providing stability and support for electronic components.
What are the benefits of glass substrate?
Glass substrates offer several advantages, including high thermal conductivity, excellent electrical insulation, dimensional stability, and compatibility with advanced packaging technologies. They contribute to the performance, reliability, and miniaturization of electronic devices.
Who makes glass substrate?
Several companies manufacture glass substrates, including Corning Incorporated, AGC Inc. (formerly Asahi Glass Co., Ltd.), SCHOTT AG, Nippon Electric Glass Co., Ltd. (NEG), and Ohara Corporation, among others.
What advantages does a glass substrate package offer?
Glass substrate packages provide superior thermal management, electrical insulation, and compatibility with advanced packaging processes, contributing to the performance and reliability of electronic devices.
Which industries utilize glass substrate packages?
Glass substrate packages find applications in semiconductor and electronics, optoelectronics and photonics, medical devices and healthcare, as well as aerospace and defense industries.
Who are some leading manufacturers of glass substrate packages?
Major players in glass substrate manufacturing include Corning Incorporated, AGC Inc., SCHOTT AG, Nippon Electric Glass Co., Ltd. (NEG), and Ohara Corporation, among others.
What are some key considerations in selecting a glass substrate package?
Considerations include material properties required for specific applications, compatibility with packaging processes, manufacturing processes, environmental impact, and compliance with industry regulations.
How do glass substrate packages contribute to environmental sustainability?