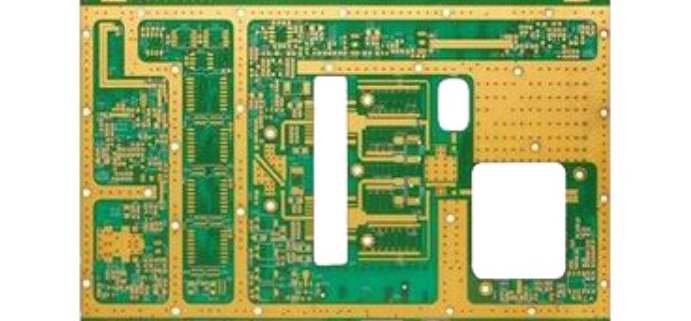
Differences Between FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, and Aluminum PCB
In the world of electronics, PCB materials play a crucial role in determining the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of electronic devices. Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of nearly all modern electronics, connecting components and ensuring proper signal flow. Among the various PCB materials available, FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, and Aluminum PCB are three of the most commonly used. Each of these materials has unique properties that make them suitable for different applications. FR4 PCB is widely used due to its affordability and reliable performance in general electronics. Rogers PCB, on the other hand, is known for its superior high-frequency performance, making it ideal for specialized applications like RF circuits and telecommunications. Lastly, Aluminum PCB offers excellent thermal management, making it perfect for high-power applications such as LED lighting. This article will compare the differences between these materials and explore their respective applications in various industries.
Overview of FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, and Aluminum PCB
What is FR4?
FR4 PCB is a widely used printed circuit board material composed of woven fiberglass cloth and epoxy resin. The combination of these materials provides FR4 with strong mechanical properties, excellent electrical insulation, and a high level of durability. This composite material is the industry standard for most general-purpose applications in electronics due to its affordability and reliable performance.
Properties of FR4
FR4’s strength, electrical insulation, and affordability make it a popular choice for various industries. The fiberglass cloth provides structural integrity, while the epoxy resin ensures electrical insulation. FR4 also offers heat resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of temperature conditions. Despite these properties, FR4 PCB does not perform as well under high-frequency or high-power conditions compared to other materials like Rogers PCB or Aluminum PCB.
Advantages of FR4 PCB
The primary advantage of FR4 PCB is its cost-effectiveness. It is widely available and can be manufactured at a low cost, making it ideal for general-purpose applications where performance requirements are less demanding. FR4 PCB offers good electrical insulation and heat resistance, making it suitable for most standard consumer electronics and industrial equipment.
Disadvantages of FR4 PCB
FR4 PCB has some limitations. It is not ideal for high-frequency applications due to its higher dielectric loss compared to materials like Rogers PCB, which is specifically designed for high-speed circuits. Additionally, FR4 has lower thermal conductivity, meaning it struggles to manage heat in high-power applications, unlike Aluminum PCB, which is better suited for thermal dissipation.
Common Applications
FR4 PCB is commonly used in consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and basic consumer devices. Its affordability and reliable performance make it an ideal choice for low-cost, everyday electronics that do not require the advanced properties of Rogers PCB or Aluminum PCB.
Overview of Rogers PCB, FR4 PCB, and Aluminum PCB
What is Rogers PCB?
Rogers PCB refers to a type of printed circuit board that is made from advanced materials such as PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), ceramics, or composites. Unlike FR4 PCB, which uses fiberglass and epoxy resin, Rogers PCB utilizes these high-performance materials to achieve exceptional electrical and mechanical properties. The use of PTFE and ceramics allows Rogers PCB to perform exceptionally well in high-frequency, high-speed applications, making it ideal for cutting-edge electronic systems.
Advantages of Rogers PCB
The main advantages of Rogers PCB lie in its superior performance in demanding applications. It excels in high-frequency and high-speed environments due to its low dielectric loss, ensuring signal integrity is maintained even in complex systems. This is a significant improvement over FR4 PCB, which struggles with signal loss in high-frequency applications. Additionally, Rogers PCB has superior thermal conductivity, making it capable of dissipating heat efficiently compared to FR4 PCB and even Aluminum PCB in some cases, especially in high-speed electronics. It also offers stable performance across a wide range of temperatures, making it ideal for aerospace and telecommunications applications, where environmental conditions can vary significantly.
Disadvantages of Rogers PCB
Despite its high performance, Rogers PCB comes with a few disadvantages. The most notable is its higher cost compared to FR4 PCB. The advanced materials used in Rogers PCBs make them significantly more expensive, which can be a drawback for cost-sensitive projects. Additionally, Rogers PCB is more challenging to process than FR4 PCB, requiring specialized manufacturing techniques that increase production complexity and cost.
Common Applications
Rogers PCB is commonly used in applications that require high-frequency and high-speed performance, such as RF (radio frequency) and microwave devices. It is also favored in high-speed circuits used in telecommunications, aerospace, and other advanced electronic systems. Due to its superior thermal management and stable electrical properties, Rogers PCB is the material of choice for applications where performance is critical, and the benefits outweigh the higher cost compared to FR4 PCB and Aluminum PCB.
Overview of FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, and Aluminum PCB
What is Aluminum PCB?
Aluminum PCB is a type of metal-core printed circuit board (PCB) that uses aluminum as its substrate material. Unlike FR4 PCB or Rogers PCB, which typically use fiberglass or composite materials, Aluminum PCB incorporates a metal core, usually aluminum, to enhance its heat dissipation properties. The aluminum substrate provides a robust base, making it suitable for applications that generate significant heat. This unique structure allows Aluminum PCB to efficiently manage high-power circuits, where thermal management is a primary concern.
Advantages of Aluminum PCB
One of the primary advantages of Aluminum PCB is its superior heat dissipation capabilities. The metal core acts as a heat sink, effectively transferring heat away from the components, preventing overheating and ensuring long-term reliability. This makes Aluminum PCB an ideal choice for high-power applications where heat generation is substantial, such as power electronics. In addition to its thermal advantages, Aluminum PCB is lightweight and durable, which enhances its overall performance in demanding environments. This material is well-suited for applications that require both high mechanical strength and efficient thermal management, setting it apart from materials like FR4 PCB and Rogers PCB, which may struggle in high-heat environments.
Disadvantages of Aluminum PCB
Despite its many benefits, Aluminum PCB does come with some drawbacks. It is generally more expensive than FR4 PCB due to the cost of aluminum and the specialized manufacturing processes required. Moreover, Aluminum PCB is more challenging to manufacture compared to traditional PCBs, such as FR4 PCB, because of the need to integrate a metal core and the additional complexity in the production process. These factors contribute to higher production costs and longer lead times.
Common Applications
Aluminum PCB is most commonly used in applications that require excellent thermal management, such as LED lighting, power electronics, and automotive electronics. In the LED industry, for instance, Aluminum PCB is used to mount high-power LEDs, where heat dissipation is critical for maintaining optimal performance. Similarly, Aluminum PCB is employed in power supply circuits and automotive systems, where both heat management and durability are crucial. Although Aluminum PCB may not be suitable for high-frequency applications like Rogers PCB, it is a preferred choice in industries where thermal performance is paramount.
Key Differences Between FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, and Aluminum PCB
When selecting the right PCB material, understanding the key differences between FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, and Aluminum PCB is crucial for meeting specific performance and cost requirements. Here, we’ll break down the most important factors, including material composition, performance in high-frequency applications, thermal management, and cost comparison.
Material Composition of FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, and Aluminum PCB
- FR4 PCB: FR4 PCB is made from a combination of epoxy resin and fiberglass cloth, creating a robust and cost-effective material. The resin provides electrical insulation, while the fiberglass adds strength and durability, making it suitable for general-purpose applications.
- Rogers PCB: Rogers PCB utilizes advanced materials like PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) and ceramic composites. These materials are engineered to provide excellent electrical performance, especially in high-frequency circuits. The use of PTFE and ceramics enhances the dielectric properties of Rogers PCB, making it ideal for more specialized applications that demand low-loss, high-speed signal transmission.
- Aluminum PCB: Aluminum PCB incorporates an aluminum metal core, which significantly improves its ability to dissipate heat. The metal substrate is combined with a dielectric layer and a copper layer to form the complete PCB. This structure provides durability and excellent thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications where heat management is a critical factor.
Performance in High-Frequency Applications: FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, and Aluminum PCB
- FR4 PCB: FR4 PCB offers limited performance in high-frequency applications. Its higher dielectric loss can cause signal degradation when used for high-speed or high-frequency circuits, such as RF (radio frequency) and microwave applications.
- Rogers PCB: Rogers PCB is specifically designed for high-frequency, low-loss performance. Thanks to its use of materials like PTFE and ceramics, Rogers PCB offers excellent electrical properties, such as low signal attenuation, making it ideal for high-speed and high-frequency applications like RF circuits and telecommunications.
- Aluminum PCB: Aluminum PCB is generally not used for RF applications due to its material properties, which are not optimized for high-frequency signal transmission. However, it excels in high-power devices that require efficient heat dissipation, such as power electronics and LED lighting.
Thermal Management: FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, and Aluminum PCB
- FR4 PCB: FR4 PCB has moderate thermal management capabilities. While it offers basic heat resistance, its thermal conductivity is relatively low compared to other materials. This limits its use in high-power applications where heat dissipation is a critical factor.
- Rogers PCB: Rogers PCB provides excellent thermal properties, especially in high-speed circuits. The materials used in Rogers PCB, like PTFE and ceramic composites, have lower dielectric loss and better heat resistance, making them ideal for environments where both thermal and electrical performance are important.
- Aluminum PCB: Aluminum PCB excels in thermal management, thanks to its metal core. The aluminum substrate acts as a heat sink, efficiently transferring heat away from the components. This makes Aluminum PCB an excellent choice for high-power applications like LED lighting and power electronics, where heat dissipation is essential.
Cost Comparison: FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, and Aluminum PCB
- FR4 PCB: FR4 PCB is the most affordable option of the three, making it an ideal choice for cost-sensitive applications. Its material composition and widespread availability allow for economical manufacturing, making it perfect for general-purpose electronics and basic consumer devices.
- Rogers PCB: Rogers PCB is more expensive than FR4 PCB due to its advanced material properties, such as PTFE and ceramics. The higher performance characteristics come at a cost, making Rogers PCB more suitable for high-end applications where performance outweighs the budget, such as RF and high-speed circuits.
- Aluminum PCB: Aluminum PCB is more expensive than FR4 PCB, though generally less costly than Rogers PCB. The use of aluminum as a metal core adds to the production cost, and the manufacturing process is more complex. However, the thermal benefits it provides in high-power applications justify the added cost in certain industries like automotive and LED lighting.
These key differences between FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, and Aluminum PCB highlight how material composition, performance in specific applications, and thermal management capabilities influence the choice of PCB material for various electronic devices. By understanding these factors, manufacturers can make more informed decisions based on their specific needs, balancing performance requirements with budget constraints.
Applications and Choosing the Right PCB: FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, and Aluminum PCB
Selecting the right PCB material is crucial for ensuring the performance, reliability, and efficiency of electronic devices. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as signal integrity, thermal management, and cost constraints. Below, we explore when to use FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, and Aluminum PCB based on their unique characteristics.
When to Use FR4 PCBs
FR4 PCB is the most widely used PCB material, particularly for general-purpose electronics. It is ideal for low-cost applications where performance requirements are standard and not highly demanding. FR4 PCB is commonly used in simple consumer devices like smartphones, televisions, and home appliances, where the electrical properties are sufficient, and thermal management is not a major concern. Due to its affordability and availability, FR4 PCB is the material of choice for mass-produced products where cost-effectiveness is a key consideration. Additionally, FR4 PCB is also suitable for industrial equipment and automotive applications that do not require high-frequency operation or extreme heat dissipation.
When to Use Rogers PCBs
Rogers PCB is the go-to material for high-performance applications that demand superior electrical properties, particularly in high-frequency and high-speed environments. If your application involves RF circuits, microwave communication, or aerospace technologies, Rogers PCB is the best choice. The unique combination of PTFE and ceramic composites in Rogers PCB allows it to maintain signal integrity with minimal loss, even at high frequencies, making it ideal for advanced communication systems. Rogers PCB is also commonly used in telecommunications, satellite systems, and high-speed data processing circuits, where precision and low-loss performance are critical. While Rogers PCB is more expensive than FR4 PCB, its unmatched performance in specialized applications justifies the higher cost.
When to Use Aluminum PCBs
Aluminum PCB is the ideal material for applications that require efficient thermal management. The aluminum metal core provides superior heat dissipation, making Aluminum PCB the best option for high-power devices, where excessive heat generation could damage components. Aluminum PCB is extensively used in LED lighting systems, where high-powered LEDs generate a significant amount of heat. By using Aluminum PCB, the heat is efficiently transferred away from the LEDs, ensuring longer lifespan and better performance. Additionally, Aluminum PCB is used in power supplies, automotive electronics, and power amplifiers, where heat dissipation is crucial for stable and reliable operation. While Aluminum PCB is more expensive than FR4 PCB, it is still more affordable than Rogers PCB, making it a cost-effective choice for thermal-heavy applications.
Choosing the right PCB material—whether FR4 PCB, Rogers PCB, or Aluminum PCB—depends on the specific needs of your application. FR4 PCB is ideal for low-cost, general-purpose electronics, while Rogers PCB excels in high-frequency and high-speed applications that require advanced signal integrity. Aluminum PCB shines in high-power applications where superior heat dissipation is essential. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each material, you can make an informed decision that optimizes both performance and cost for your electronic device.
FQAs Abut FR4 PCB Rogers PCB Aluminum PCB
What is the difference between Rogers and FR4 PCB?
The key difference between Rogers PCB and FR4 PCB lies in the materials used and their performance characteristics. FR4 PCB is made from a combination of epoxy resin and fiberglass, making it suitable for general-purpose applications and cost-effective solutions. However, it has limitations in high-frequency and high-speed circuits due to its higher dielectric loss and lower signal integrity.
Rogers PCB is made from advanced materials like PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) and ceramics, designed specifically for high-frequency and high-speed applications. Rogers PCB offers superior electrical performance with low signal loss, low dielectric constant, and high thermal stability, making it ideal for RF circuits, telecommunications, and aerospace applications.
What material is Rogers PCB made of?
Rogers PCB is primarily made of PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), a high-performance polymer, and ceramic composites. These materials provide superior dielectric properties, making Rogers PCB highly effective for high-frequency, high-speed, and low-loss applications. PTFE offers excellent insulation properties, while ceramic fillers enhance the thermal stability and mechanical strength of the PCB.
What are the disadvantages of FR4?
While FR4 PCB is widely used for its cost-effectiveness and general-purpose applications, it does have several disadvantages:
- Limited performance for high-frequency signals: FR4 PCB has higher dielectric loss, which can lead to signal degradation in high-frequency applications.
- Lower thermal conductivity: Compared to Rogers PCB or Aluminum PCB, FR4 PCB is less effective at dissipating heat, which can limit its use in power electronics or high-speed circuits.
- Not ideal for high-speed or high-power applications: FR4 PCB is less suitable for advanced applications that demand high signal integrity, fast processing speeds, or thermal management.
Which material is commonly used for RF PCBs: FR4, Rogers, Aluminum, or Steel?
For RF (radio frequency) applications, Rogers PCB is the most commonly used material. This is because Rogers PCB is specifically designed for high-frequency, low-loss performance, making it ideal for RF circuits, microwave communication, and telecommunications. The advanced materials used in Rogers PCB (such as PTFE and ceramics) provide low dielectric constant and low signal attenuation, which is crucial for RF performance.
While FR4 PCB is cheaper and commonly used for general applications, its performance in high-frequency environments is limited. Aluminum PCB is typically used for thermal management in high-power applications, such as LED lighting, but not for RF. Steel is not commonly used for PCBs due to its poor electrical and thermal properties compared to Rogers PCB and FR4 PCB.