COB Technology: Enhancing Performance, Reducing Footprint
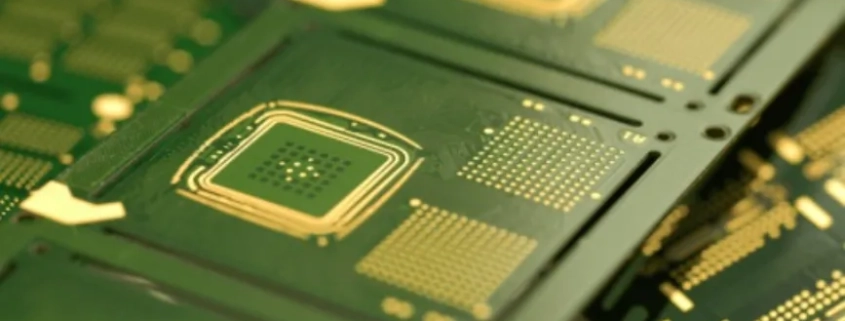
Chip on Board (COB) technology revolutionizes traditional electronic packaging by directly mounting semiconductor chips onto a substrate. This method eliminates the need for individual packaging, leading to a compact, efficient design. COB has evolved from its inception in the late 20th century to become a cornerstone of modern electronics, offering significant advancements in miniaturization, performance, and reliability. Its application extends beyond electronics, particularly in LED lighting where COB configurations deliver unparalleled brightness and energy efficiency. Moreover, COB technology finds utility in various fields like automotive, medical devices, and consumer electronics, emphasizing its versatility and indispensability in contemporary engineering.
Illuminating the Role of Chip on Board in LED Lighting
Chip on Board (COB) technology plays a pivotal role in the advancement of LED lighting systems, offering numerous advantages over traditional lighting solutions.
Enhanced Brightness and Efficiency
COB LEDs are renowned for their exceptional brightness and efficiency. By directly mounting multiple LED chips onto a single substrate, COB configurations enable higher lumen output per unit area compared to conventional LEDs. This concentrated light output translates to brighter illumination, making COB LEDs ideal for applications requiring high-intensity lighting, such as stadium lighting, automotive headlights, and stage lighting.
Compact Design and Thermal Management
The compact design of COB LEDs allows for greater flexibility in luminaire design and integration. Unlike traditional LED packages, which require additional space for individual packaging, COB LEDs offer a more streamlined form factor, facilitating sleeker and more aesthetically pleasing lighting fixtures. Furthermore, COB technology enhances thermal management by enabling efficient heat dissipation from the LED chips to the substrate. This improved thermal performance helps prolong the lifespan of COB LEDs and ensures consistent performance even in demanding operating conditions.
In summary, the functionality of Chip on Board technology in LED lighting encompasses superior brightness, efficiency, compact design, and enhanced thermal management, making it a preferred choice for various lighting applications.
The Manufacturing Process of Chip on Board (COB)
The production of Chip on Board (COB) modules involves several intricate steps to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of COB Production
1. Substrate Preparation: The process begins with preparing the substrate, usually a ceramic or metal-core printed circuit board (PCB), to serve as the base for mounting the LED chips.
2. LED Chip Mounting: High-precision machinery is used to accurately place the LED chips onto the substrate. These chips are arranged in a closely packed array to maximize light output.
3. Wire Bonding: Once the LED chips are in place, wire bonding techniques are employed to connect the chips to the circuitry on the substrate. This step requires precision to ensure proper electrical connections.
4. Encapsulation: The bonded LED chips are then encapsulated with a protective material, such as silicone or epoxy resin, to shield them from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and mechanical stress. Encapsulation also helps in heat dissipation and electrical insulation.
5. Curing and Testing: After encapsulation, the modules undergo curing processes to solidify the encapsulant. Quality control measures, including visual inspection and electrical testing, are conducted to identify any defects or irregularities.
Mounting LEDs Directly onto a Circuit Board
Unlike traditional LED packaging methods where individual LED components are mounted onto a separate package, COB technology involves mounting the LED chips directly onto the substrate without the need for individual packages. This direct mounting approach reduces the overall size of the LED module and enhances thermal management by enabling efficient heat dissipation.
Wire Bonding and Encapsulation Techniques
Wire bonding is a critical step in COB production where fine wires are used to establish electrical connections between the LED chips and the substrate. This process requires precision equipment to ensure accurate placement and bonding of the wires. Following wire bonding, the LED chips are encapsulated with a protective material to safeguard them from external elements and provide structural support.
Quality Control Measures and Testing Protocols
Throughout the manufacturing process, stringent quality control measures are implemented to maintain the highest standards of product quality and reliability. Visual inspections, automated optical inspection (AOI), and electrical testing are conducted at various stages to detect any defects or inconsistencies. Additionally, random sampling and rigorous testing protocols are employed to validate the performance and durability of COB modules before they are released for commercial use.
Distinguishing Chip on Board (COB) on a Circuit Board
Chip on Board (COB) technology offers distinct advantages over traditional surface-mounted devices (SMDs) when integrated within circuitry.
Understanding the Integration of COB within Circuitry
COB modules are integrated directly onto the circuit board, with the LED chips mounted directly onto the substrate. This integration eliminates the need for individual LED packages, resulting in a more streamlined and compact design. COB modules can be seamlessly integrated into various electronic devices and lighting fixtures, offering versatility and ease of assembly.
Comparison with Traditional Surface-Mounted Devices (SMDs)
In contrast to COB technology, traditional surface-mounted devices (SMDs) involve mounting individual LED components onto the surface of the circuit board. While SMDs are suitable for certain applications, they often require additional space for packaging and thermal management. COB technology eliminates the packaging step by mounting the LED chips directly onto the substrate, resulting in a more efficient use of space and improved thermal performance.
Advantages of COB in Terms of Size, Performance, and Reliability
COB technology offers several advantages over SMDs in terms of size, performance, and reliability:
– Size: COB modules have a smaller form factor compared to SMDs, allowing for more compact and space-saving designs.
– Performance: COB modules typically exhibit higher lumen output and better light uniformity compared to SMDs. The direct mounting of LED chips onto the substrate minimizes thermal resistance, resulting in improved heat dissipation and enhanced performance.
– Reliability: The absence of individual LED packages in COB modules reduces the risk of solder joint failures and improves overall reliability. Additionally, COB modules undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure consistent performance and longevity.
In summary, the integration of Chip on Board technology within circuitry offers advantages such as compact size, superior performance, and enhanced reliability compared to traditional surface-mounted devices.
Exploring On-Board vs. On-Chip Components
Understanding the distinctions between on-board and on-chip components provides insight into their respective roles and significance in electronic systems, particularly in the context of Chip on Board (COB) technology.
Clarifying the Difference Between On-Board and On-Chip Components
– On-Board Components: On-board components refer to electronic elements that are mounted directly onto the circuit board, such as resistors, capacitors, and connectors. These components are typically soldered onto the board’s surface and play essential roles in providing functionality, connectivity, and support to the overall electronic system.
– On-Chip Components: On-chip components, on the other hand, are integrated directly onto the semiconductor chip itself during the fabrication process. These components are built into the chip’s architecture and include transistors, diodes, and other active and passive elements. On-chip components are fundamental to the operation of integrated circuits (ICs) and semiconductor devices, enabling functions such as signal processing, amplification, and logic operations.
Role of On-Board Components in COB Technology
In COB technology, on-board components complement the LED chips mounted directly onto the substrate. On-board components may include drivers, resistors, and thermal management elements, which are essential for regulating power, controlling current flow, and managing heat dissipation within the COB module. These components contribute to the overall functionality, stability, and performance of the COB lighting system, ensuring optimal operation and reliability.
Significance of On-Chip Components in Semiconductor Design
In semiconductor design, on-chip components are fundamental building blocks that determine the functionality and performance of integrated circuits. On-chip components are fabricated using semiconductor manufacturing processes, allowing for precise control over their characteristics and properties. Advances in semiconductor technology have led to the integration of increasingly complex on-chip components, enabling the development of highly integrated and multifunctional semiconductor devices.
In summary, while on-board components play a vital role in supporting and enhancing the functionality of COB modules, on-chip components are essential for semiconductor design, providing the foundation for the development of integrated circuits and semiconductor devices. Understanding the distinction and significance of these components is crucial for optimizing the performance and reliability of electronic systems incorporating COB technology.
Applications and Benefits of Chip on Board Technology
Chip on Board (COB) technology offers a wide range of applications and benefits across various industries, making it a versatile and highly sought-after solution.
Versatility Across Various Industries
COB technology finds extensive use in lighting, automotive, electronics, and numerous other sectors due to its compact design, high performance, and reliability. In the lighting industry, COB LEDs are widely utilized for general illumination, architectural lighting, and specialty applications such as grow lights and stage lighting. In automotive applications, COB modules are employed in headlights, taillights, and interior lighting fixtures, offering superior brightness and energy efficiency. Additionally, COB technology is utilized in consumer electronics, industrial equipment, medical devices, and signage, showcasing its adaptability across diverse industries.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Sustainability
One of the primary advantages of COB technology is its exceptional energy efficiency. COB LEDs consume less power while delivering higher lumen output compared to traditional lighting sources, resulting in significant energy savings and reduced carbon emissions. The superior thermal management of COB modules further enhances their energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss and improving overall performance. Additionally, the longevity of COB LEDs reduces the need for frequent replacements, contributing to lower maintenance costs and reduced waste, thus promoting environmental sustainability.
Cost-Effectiveness and Long-Term Reliability
COB technology offers cost-effective solutions for lighting and electronic applications, thanks to its streamlined design, simplified manufacturing process, and high-volume production capabilities. The integration of multiple LED chips onto a single substrate reduces material and labor costs associated with traditional LED packaging methods. Furthermore, COB modules exhibit exceptional reliability and durability, resulting in longer lifespans and reduced downtime for maintenance and replacement. This long-term reliability translates to lower total cost of ownership and enhanced return on investment for end-users across various industries.
In summary, Chip on Board technology offers versatile applications, energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and long-term reliability, making it an ideal choice for a wide range of lighting, automotive, and electronic applications. Its continued advancements and widespread adoption are poised to drive innovation and efficiency across industries in the years to come.
FAQs about chip on board process
The function of chip on board (COB) is to directly mount semiconductor chips onto a substrate, eliminating the need for individual packaging. This results in a compact, efficient design with enhanced performance and reliability.
To make a chip on board (COB), the process involves several steps: preparing the substrate, mounting LED chips directly onto the substrate, wire bonding to establish electrical connections, encapsulating the chips for protection, and conducting quality control testing to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
A chip on a circuit board refers to an integrated circuit or semiconductor chip that is mounted onto a printed circuit board (PCB) to provide specific functionality within an electronic system. These chips can include microprocessors, memory chips, or other semiconductor devices.
“On board” typically refers to electronic components that are mounted directly onto a circuit board, such as resistors, capacitors, and connectors. “On chip,” on the other hand, refers to components that are integrated directly onto the semiconductor chip itself during the fabrication process, such as transistors, diodes, and other active and passive elements.